Explain the different types of CPU scheduling algorithms in Operating System.
In a multi-process operating system, the resource allocation algorithm is known as the Banker's Algorithm. It is utilized to manage resource allocation. It's used to make sure that a group of programs on a single computer can share the resources they have (like CPU time, memory, I/O devices, etc.).Read more
In a multi-process operating system, the resource allocation algorithm is known as the Banker’s Algorithm. It is utilized to manage resource allocation. It’s used to make sure that a group of programs on a single computer can share the resources they have (like CPU time, memory, I/O devices, etc.). fairly and effectively.
The Investor’s Calculation works by reproducing a ledger for each interaction, where the assets distributed to the cycle are treated as stores into the record. The process’s “funds,” or resources, are checked by the algorithm to see if they are sufficient to allocate the requested resources. In the event that it does, the allocation is carried out, and the process’s account is updated in line with this. The allocation is stopped until sufficient resources are available.
The algorithm ensures that no process can acquire more resources than it has been allocated and that no process can exceed its resources. This ensures that processes can run safely and effectively while also preventing deadlocks.
See less
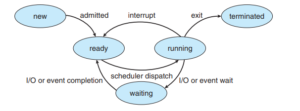
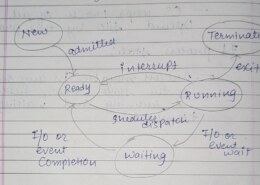
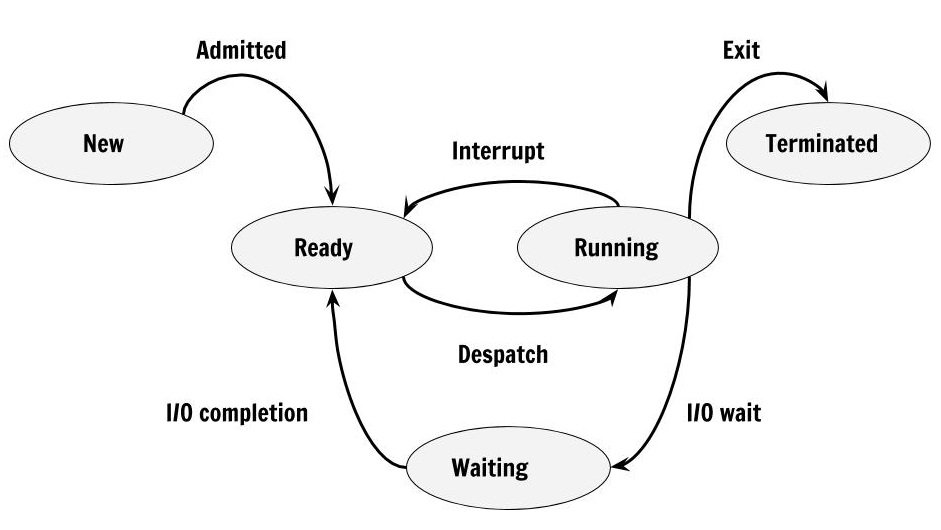
First Come First Serve First Come First Serve is the full form of FCFS. It is the easiest and most simple CPU scheduling algorithm. In this type of algorithm, the process which requests the CPU gets the CPU allocation first. This scheduling method can be managed with a FIFO queue. Shortest RemainingRead more
First Come First Serve
First Come First Serve is the full form of FCFS. It is the easiest and most simple CPU scheduling algorithm. In this type of algorithm, the process which requests the CPU gets the CPU allocation first. This scheduling method can be managed with a FIFO queue.
Shortest Remaining Time
The full form of SRT is Shortest remaining time. It is also known as SJF preemptive scheduling. In this method, the process will be allocated to the task, which is closest to its completion. This method prevents a newer ready state process from holding the completion of an older process.
Priority Based Scheduling
priority scheduling is a method of scheduling processes based on priority. In this method, the scheduler selects the tasks to work as per the priority.
Priority scheduling also helps OS to involve priority assignments. The processes with higher priority should be carried out first, whereas jobs with equal priorities are carried out on a round-robin or FCFS basis. Priority can be decided based on memory requirements, time requirements, etc.
As the process enters the ready queue, its PCB (Process Control Block) is linked with the tail of the queue. So, when CPU becomes free, it should be assigned to the process at the beginning of the queue.
Round-Robin Scheduling
Round robin is the oldest, simplest scheduling algorithm. The name of this algorithm comes from the round-robin principle, where each person gets an equal share of something in turn. It is mostly used for scheduling algorithms in multitasking. This algorithm method helps for starvation free execution of processes.
Shortest Job First
SJF is a full form of (Shortest job first) is a scheduling algorithm in which the process with the shortest execution time should be selected for execution next. This scheduling method can be preemptive or non-preemptive. It significantly reduces the average waiting time for other processes awaiting execution.
Shortest Job First
SJF is a full form of (Shortest job first) is a scheduling algorithm in which the process with the shortest execution time should be selected for execution next. This scheduling method can be preemptive or non-preemptive. It significantly reduces the average waiting time for other processes awaiting execution.
See less