Discuss the role of blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrency, and provide examples of its practical applications.
Blockchain technology's decentralized nature is revolutionizing cybersecurity in several key ways: 1. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain operates as a distributed ledger, meaning that data is stored across a network of computers (nodes) rather than a single central server. This makes it much moreRead more
Blockchain technology’s decentralized nature is revolutionizing cybersecurity in several key ways:
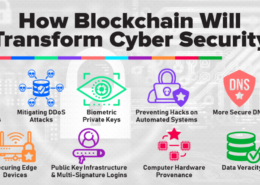
1. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain operates as a distributed ledger, meaning that data is stored across a network of computers (nodes) rather than a single central server. This makes it much more difficult for hackers to attack because there is no single point of failure. Compromising the network would require simultaneously attacking a majority of the nodes.
2. Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it is extremely difficult to alter. This immutability helps prevent unauthorized changes and tampering. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain of information.
3. Transparency and Traceability: Transactions on a blockchain are transparent and can be traced back to their origin. This transparency deters fraudulent activities and enhances trust, as all participants can see the same information and verify it independently.
4. Decentralized Consensus: Blockchain uses consensus mechanisms (such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to validate transactions. This means that no single entity controls the verification process, reducing the risk of corruption or manipulation.
5. Enhanced Security Protocols: Blockchain technology employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Public and private keys, along with digital signatures, ensure that only authorized users can access and execute transactions.
6. Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute agreements when predetermined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and enhancing security through automation.
By decentralizing data storage and verification, blockchain technology significantly enhances cybersecurity, making systems more resilient to attacks, reducing fraud, and increasing trust among users.
See less
While the technology of blockchain has primarily been linked to the powering of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it has broadened into much more than that single use. At its core, blockchain provides a peer-to-peer, incorruptible, and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions, hence quitRead more
While the technology of blockchain has primarily been linked to the powering of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it has broadened into much more than that single use. At its core, blockchain provides a peer-to-peer, incorruptible, and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions, hence quite wide in its application. In supply chain management, tracing becomes more evident in the fact that entities can track products from source to destination, hence ensuring authenticity and thereby reducing cases of fraud. It secures patient records in healthcare, letting information from the different medical providers flow freely to one another while protecting the privacy of the patients. It is being utilized by financial services for a quicker, more inexpensive, and highly secure transaction process without the need for middlemen. Blockchain has further found applications in the voting systems, providing tamperproof and transparent election processes, and in intellectual property, say, protecting digital assets and intellectual property rights. Blockchain makes real estate transactions easier, with reduced fraud and clearer property records. Additionally, blockchain smart contracts automate the execution of contract terms without requiring an intermediary, making a wide array of business processes more efficient and building up trust in those business processes. Overall, blockchain technology is able to provide secure, transparent, and decentralized options, allowing it to be extremely powerful across multiple industries.
See less