What ethical considerations arise from the development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) across various sectors? Specifically, how do issues related to privacy, data security, and surveillance impact individuals and society? What are the potential biases embedded in AI algorithms, ...
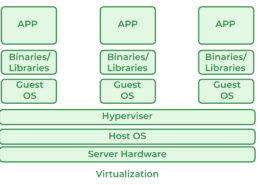
Virtualization is a technology that creates virtual instances of physical hardware resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networks. It allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own operating system and applications. This is achieved through aRead more
Virtualization is a technology that creates virtual instances of physical hardware resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networks. It allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own operating system and applications. This is achieved through a software layer called a hypervisor, which manages and allocates resources to each VM.
- Key Concepts:
- Hypervisor: Software that enables multiple VMs to run on a single physical machine. Types include Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted).
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Independent instances that run their own operating systems and applications, sharing the underlying physical hardware.
- Benefits in Cloud Computing:
Top 3 Benefits:
- Resource Efficiency: Virtualization maximizes the use of physical hardware by allowing multiple VMs to run on a single server, reducing the need for additional hardware.
- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware requirements lead to lower capital and operational expenses, including energy consumption and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Virtualization allows for easy scaling of resources. New VMs can be quickly created to handle increased demand, and redundant VMs can be removed when demand decreases.
Other Benefits:
Isolation and Security, Enhanced Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity and Flexibility etc.
Virtualization is a cornerstone of cloud computing, enabling efficient, flexible, and cost-effective resource management.
See less
The development and use of artificial intelligence (AI) raise several ethical concerns that impact individuals and society: 1. **Privacy and Surveillance**: AI often requires large amounts of data, which can threaten personal privacy. AI can also enhance surveillance, leading to concerns about invasRead more
The development and use of artificial intelligence (AI) raise several ethical concerns that impact individuals and society:
1. **Privacy and Surveillance**: AI often requires large amounts of data, which can threaten personal privacy. AI can also enhance surveillance, leading to concerns about invasive monitoring and loss of civil liberties.
2. **Bias and Fairness**: AI systems can inherit biases from their training data, leading to unfair treatment of people based on race, gender, or other factors. Ensuring AI fairness requires diverse data and regular monitoring to detect and correct biases.
3. **Accountability and Transparency**: It’s important to know how AI systems make decisions and who is responsible when things go wrong. Clear explanations and accountability are crucial for building trust in AI technologies.
4. **Impact on Jobs**: AI can automate many jobs, potentially causing job loss. Preparing workers through retraining and education is essential to help them transition to new roles created by AI advancements.
5. **Military Use**: AI in weapons and military applications raises serious ethical issues, including the risk of loss of human control in critical situations. Regulations are needed to ensure ethical use in warfare.
6. **Regulation and Ethics**: Governments should create rules to ensure AI development respects human values, fairness, and human rights. This includes setting standards and enforcing compliance to protect against misuse.
By addressing these ethical issues, we can ensure AI benefits everyone while minimizing risks and protecting fundamental rights.
See less