Imagine you have two types of toy boxes: one called "List" and the other called "Set." Each box holds your toy cars, but they follow different rules. List A List is like a special toy box where you can keep your toy cars in a specific order. When you put a car in, it stays where you put it. If you pRead more
Imagine you have two types of toy boxes: one called “List” and the other called “Set.” Each box holds your toy cars, but they follow different rules.
List
A List is like a special toy box where you can keep your toy cars in a specific order. When you put a car in, it stays where you put it. If you put a red car first, then a blue car, and then a green car, they will always stay in that order: red, blue, green.
- Order: The order you put your cars in matters.
- Duplicates: You can have more than one of the same car. If you have three red cars, you can put all three in your List box.
Set
A Set is like a magical toy box where the order doesn’t matter, and you can’t have duplicate cars. If you put a red car in, then a blue car, and then another red car, the box will only keep one red car and one blue car.
- No Order: The cars don’t stay in the order you put them in.
- No Duplicates: You can only have one of each car. If you try to put in two red cars, the Set box will only keep one.
Summary
- List: Keeps things in the order you put them and allows duplicates.
- Set: Doesn’t care about order and only keeps one of each item.
So, if you like to keep your toys in a specific order and have multiple of the same toy, use a List. If you want to make sure you only have one of each toy and don’t care about the order, use a Set.
See less
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Definition: AI is the broadest concept that involves creating machines or systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and understanding natural language. Examples: VirtualRead more
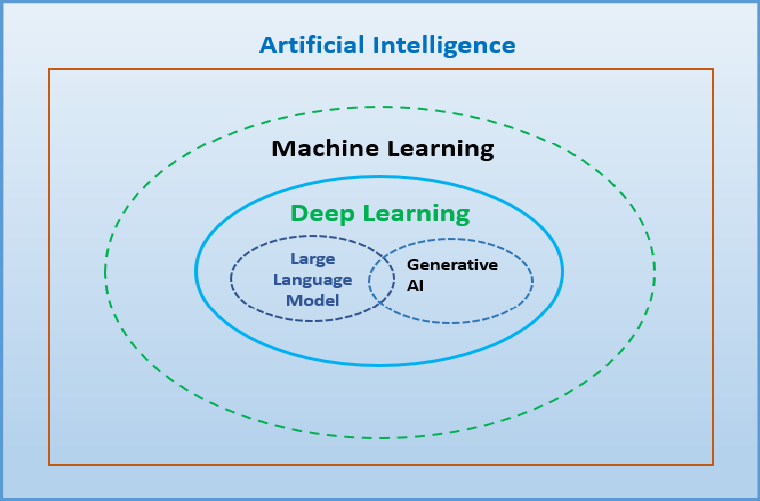
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Definition: AI is the broadest concept that involves creating machines or systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and understanding natural language.
Examples:
Machine Learning (ML)
Definition: ML is a subset of AI that involves the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Instead of being explicitly programmed to perform a task, ML models improve their performance through experience (data).
Examples:
Deep Learning (DL)
Definition: DL is a subset of ML that involves neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks). It aims to model complex patterns in data using multiple layers of abstraction.
Examples:
See less