Discuss the potential benefits and ethical challenges of integrating artificial intelligence in healthcare delivery systems. How can policymakers ensure equitable access to AI-driven healthcare technologies in diverse socio-economic contexts?
Mains Answer Writing Latest Questions
What role does national income accounting play? Talk about the numerous elements that influence a nation’s GDP. (Answer in 200 words)
-
This answer was edited.
1. Transparent Allocation: Clear budget allocations can reduce opportunities for misallocation and bribery. 2. Public Disclosure: Regularly publishing budget details increase public scrutiny and accountability. 3. Oversight Institutions: Strong institutions like the CAG and PAC help audit and review expenditures. 4. E-Governance: Digital ...
-
How the Budget System Can Contribute to Corruption: Opacity and Lack of Transparency: Complex Budgetary Processes: Beneath the apparently clear and rational system, budgeting may involve a number of susceptible and unclear steps, with little public participation/transparency. This lack of transparenRead more
How the Budget System Can Contribute to Corruption:
Opacity and Lack of Transparency:
Complex Budgetary Processes: Beneath the apparently clear and rational system, budgeting may involve a number of susceptible and unclear steps, with little public participation/transparency. This lack of transparency can create opportunities for corruption, such as:
Misallocation of Funds: Money can be embezzled to give it or use it for other purposes in the best interest of some people.
Inflated Costs: Tenders and contracts can be obtained at exorbitant prices for the award givers and the real prices are paid by the officials in cash difference.
Kickbacks and Bribery: Corruption through bribery and kickbacks ensures that the particular agency is able to receive funds, convenience for budgeting and approving projects.
Limited Public Participation:Lack of Citizen Input: Deficit participation in the process of formulating its budget leads to lack of accountability and can also leads to the practice of corruption.
Lack of Public Awareness: The public cannot know where their money is being used, or when and where corruption is taking place if they are not informed about the budget.
Weak Oversight Mechanisms:Inadequate Audits: It means that weak auditing systems may not be able to pick and check cases of corruption hence making them go unreported.
Limited Accountability: Misconduct is likely to be fostered whenever there are no precautions against officials employing public funds for unauthorised purposes.
How the Budget System Can Help Prevent Corruption:Transparency and Accountability:
Open Budget Initiatives: Budgeting for and with citizens, engagement of citizens in budgetary processes, online access to budgetary paperwork, and citizen feedback forums can help reduce corruption in budget processes.
Independent Audits: Internal auditing is very useful in financial reporting irregularities since the auditing work is done by independent agencies.
Technology-Enabled Solutions:Digitalization: E-governance of the budget, wherein people use technology to manage their budget such as through control panels, is a better way of managing budgets since it specially eliminates the mechanisms for manual alteration.
Strengthening Institutions:Independent Regulatory Bodies: Improvement of the functions of independent regulatory agencies might improve the monitoring and implementation of budgetary laws and policies.
See less
Civil Society Engagement: This paper finds that active Civil Society Organization engagement in budget monitoring and advocacy can contribute to the identification and mitigation of corruption risks.
-
Governments play a crucial role in elections by establishing and enforcing regulations to ensure fair and free voting processes. They manage voter registration, maintain and update voter lists, and ensure accessibility to polling stations. Governments also oversee the training of election officials,Read more
Governments play a crucial role in elections by establishing and enforcing regulations to ensure fair and free voting processes. They manage voter registration, maintain and update voter lists, and ensure accessibility to polling stations. Governments also oversee the training of election officials, the security of the voting process, and the integrity of the ballot counting. They handle disputes and certify election results. Additionally, governments often conduct voter education campaigns to inform citizens about their rights and the importance of voting. By providing these services, governments help to uphold the democratic process and ensure public confidence in election outcomes.
See less
-
Balancing the need to reduce public debt with maintaining economic growth and stability is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various economic policies and their implications. Here are key strategies, their potential risks, and the trade-offs associated with them: Strategies for RRead more
Balancing the need to reduce public debt with maintaining economic growth and stability is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various economic policies and their implications. Here are key strategies, their potential risks, and the trade-offs associated with them:
Strategies for Reducing Public Debt
1. Fiscal Consolidation
Description: This involves reducing budget deficits through spending cuts and/or tax increases.
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
Short-term Economic Contraction: Spending cuts and higher taxes can reduce aggregate demand, potentially leading to slower economic growth or even recession.
Social Impact: Cuts in public spending, especially on social services, can affect the most vulnerable populations.
Political Challenges: Fiscal consolidation can be politically unpopular, leading to resistance and instability.
2. Economic Growth
Description: Promoting economic growth increases government revenues without raising tax rates and reduces the debt-to-GDP ratio.
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
Inflation: Rapid growth can lead to inflation, which, if uncontrolled, can harm the economy.
Sustainability: Growth strategies need to be sustainable. Over-reliance on temporary growth spurts (e.g., from asset bubbles) can lead to future instability.
3. Structural Reforms
Description: Implementing reforms to improve economic efficiency and productivity (e.g., labor market reforms, regulatory simplifications).
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
Implementation Challenges: Structural reforms can be difficult to implement and may face political resistance.
Short-term Disruption: Reforms can cause short-term economic disruptions, especially if they involve significant changes to existing systems.
4. Privatization of State Assets
Description: Selling government-owned assets to raise funds.
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
One-time Solution: Privatization provides a one-time boost to revenue but does not address underlying fiscal imbalances.
Public Opposition: Selling state assets can face public and political opposition, particularly if it involves essential services.
Long-term Revenue Loss: Future government revenues may decline if profitable state-owned enterprises are privatized.
5. Debt Restructuring or Relief
Description: Negotiating with creditors to reduce the debt burden, through measures like extending payment periods or reducing interest rates.
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
Creditworthiness: Debt restructuring can damage a country’s credit rating, making future borrowing more expensive.
Investor Confidence: It may undermine investor confidence, leading to capital flight or reduced investment.
6. Inflation
Description: Allowing moderate inflation can reduce the real value of debt.
Potential Risks and Trade-offs:
Uncontrolled Inflation: If not managed carefully, inflation can spiral out of control, leading to economic instability.
Erosion of Savings: Inflation erodes the value of savings, potentially reducing consumer spending and investment.
Balancing Debt Reduction with Growth and Stability
Gradual Implementation:Phased Approach: Implementing fiscal consolidation gradually can help mitigate negative short-term impacts on growth.Stabilization Programs: Combining fiscal consolidation with measures to stabilize and stimulate the economy can help maintain growth.
Targeted Spending:Protecting Investments: Ensuring that spending cuts do not affect critical investments in infrastructure, education, and health can support long-term growth.
Efficiency Improvements: Focusing on improving the efficiency of public spending can reduce deficits without compromising essential services.
Revenue Enhancement:Broadening the Tax Base: Enhancing revenue through tax reforms that broaden the tax base and improve compliance can increase revenues without raising rates.
Progressive Taxation: Implementing progressive taxes can ensure that the burden of fiscal consolidation is shared more equitably.
Promoting Private Sector Growth:Business Environment: Creating a favorable environment for private sector investment can drive growth.
See less
Innovation and Competitiveness: Supporting innovation and competitiveness can lead to sustainable economic expansion.
Conclusion
Balancing debt reduction with economic growth and stability requires a mix of strategies tailored to the specific economic context. Policymakers need to consider the potential risks and trade-offs associated with each strategy and aim for a balanced approach that maintains social equity, promotes sustainable growth, and ensures long-term fiscal health. Engaging with stakeholders and maintaining flexibility to adjust policies as circumstances change are crucial for achieving these goals.
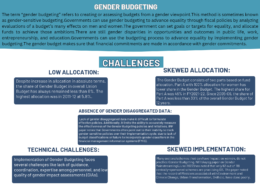
Gender budgeting: What is it? Talk about the difficulties it presents in the Indian setting. (Answer in 200 words)
-
This answer was edited.
.
Analyze the challenges India faces in balancing its desire for strategic autonomy with the need for global cooperation on issues like climate change, trade, and terrorism.
-
As India's role in the global order grows, it faces several challenges and opportunities in balancing its strategic autonomy with global cooperation. Challenges: 1. Climate Change: India needs to balance economic growth with reducing carbon emissions. This is hard because India relies on coal for enRead more

As India’s role in the global order grows, it faces several challenges and opportunities in balancing its strategic autonomy with global cooperation.
Challenges:
1. Climate Change: India needs to balance economic growth with reducing carbon emissions. This is hard because India relies on coal for energy, which conflicts with global climate goals.
2. Trade Policies: Protecting local industries while participating in global trade is tricky. India’s trade policies sometimes clash with international free trade standards.
3. Terrorism: India must work with other countries to combat terrorism. Sharing intelligence and resources is essential, but India also needs to maintain its security independence.
Opportunities:
1. Global Leadership: India can lead on issues like climate change and sustainable development, influencing global policies while protecting its interests.
2. Economic Growth: Engaging in global trade and investment can boost India’s economy, creating jobs and driving innovation.
3. Diplomatic Influence: By strengthening ties with various countries, India can enhance its diplomatic influence and navigate complex international relations.
In summary, India must balance its desire for strategic autonomy with the need for global cooperation by leveraging its growing influence, participating actively in international forums, and implementing smart domestic policies.
See less
What goals does the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act of 2003 (FRBMA) seek to achieve? List the salient qualities of it. (Answer in 200 words)
-
This answer was edited.
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 (FRBMA):- This act aims to bring the discipline in the government's finance, reduce fiscal deficit, and improve macroeconomic management (improve the management of funds with public) The Objectives of the (FRBMA) ACT,2003 are as follows : ItRead more
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
 (FRBMA):-
(FRBMA):-This act aims to bring the discipline in the government’s finance, reduce fiscal deficit, and improve macroeconomic management (improve the management of funds with public)
The Objectives of the (FRBMA) ACT,2003 are as follows :
- It reduces the Fiscal deficit: It sets targets to gradually bring down the government budget deficit. This aims for the more balanced budget.
- It eliminates a Revenue Deficit: This Act also targets on the elimination of the revenue deficit, where government spending exceeds its income. This act ensures that the Government should not rely on the borrowings to meets its expenses.
- It enhances the fiscal transparency: This act Promotes the transparency among the public by disclosing their fiscal targets and achievements. This enhances the public trust.
- It ensures debt sustainability: This Act, enables the limit on the total liabilities as a percentage of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) for the government. This act secures the upcoming generations from the excessive burden of the debt.
- It promotes macroeconomic stability: By achieving the above objectives, this act fosters to create more stable and growing economy of a country.
Functions of (FRBMA) ACT, 2003 are as follows :
- Reduce Fiscal Deficit: This act lay out specific targets for reducing Fiscal and Revenue deficit over a medium-term period. The targets are reviewed and examined periodically.
- Medium-Term Fiscal Policy statement: The government is obligated to present a medium-term fiscal policy statements which outlines it’s fiscal strategy and future projections.
- Escape cause: It sometimes allows the deviations from the targets only during the exceptional cases like natural disasters or economy downfall.
- fiscal council: An independent Fiscal Council es initially formed by this act to monitor the government’s loyalty to the targets formed by FRBMA (Fiscal Responsibility and Budget management Act.)
I am enclosing an image which describes this matter in a more significant manner and the language used is too easy to understand.
See less
Analyze the government’s initiatives to support PPPs in the construction of public infrastructure and the provision of public services, and evaluate the advantages and difficulties of this strategy with regard to effectiveness, risk-sharing, and fair service delivery.
-
Government Efforts to Promote Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) The Indian government has actively promoted Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) to enhance infrastructure development and improve the delivery of public services. This strategy aims to leverage private sector expertise, efficiency, andRead more
Government Efforts to Promote Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
The Indian government has actively promoted Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) to enhance infrastructure development and improve the delivery of public services. This strategy aims to leverage private sector expertise, efficiency, and investment capacity to complement public sector initiatives.Key Government Initiatives
Policy Frameworks and GuidelinesPPP Policy Framework: The government has established comprehensive policy frameworks and guidelines to facilitate PPP projects. This includes the Model Concession Agreement (MCA) for standardizing PPP contracts and ensuring fair risk distribution.
PPP Appraisal Committee: This committee evaluates and approves PPP projects, ensuring they meet required standards and offer public benefits.
Institutional SupportInfrastructure Development Finance Company (IDFC): Provides long-term financing for infrastructure projects.
India Infrastructure Finance Company Ltd. (IIFCL): Offers financial assistance for infrastructure projects, supporting PPPs through various financial products.
Public-Private Partnership Appraisal Committee (PPPAC): A dedicated committee to appraise and approve central sector PPP projects.
Sector-Specific InitiativesHighways and Transport: The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has utilized PPPs extensively for highway development through the Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) and Toll-Operate-Transfer (TOT) models.
Urban Development: The Smart Cities Mission promotes PPPs to develop urban infrastructure and services, including waste management, public transport, and water supply.
Healthcare: Encouraging private investment in healthcare infrastructure and services, particularly in underserved areas.
Financial Incentives and Viability Gap Funding (VGF)Viability Gap Funding Scheme: Provides financial support for PPP projects that are economically justified but not financially viable on their own.
Tax Incentives: Various tax breaks and incentives are offered to attract private investment in infrastructure projects.
Benefits of PPPs
Efficiency and ExpertisePrivate Sector Efficiency: PPPs bring in the efficiency and innovation of the private sector, often leading to cost savings and faster project completion.
Specialized Knowledge: Private entities contribute specialized knowledge and expertise, particularly in complex and technologically advanced projects.
Risk SharingShared Risks: Risks are shared between the public and private sectors, reducing the burden on government resources. This includes financial, operational, and project completion risks.
Incentive Alignment: Properly structured PPPs align the incentives of both parties, encouraging the private sector to deliver high-quality services and infrastructure.
Improved Service DeliveryEnhanced Quality: PPPs often lead to improved quality of public services through better management practices and adherence to performance standards.
Resource Mobilization: Attracting private investment helps mobilize additional resources for infrastructure development, supplementing public funds.
Economic GrowthInfrastructure Development: Enhanced infrastructure development fosters economic growth, creating jobs, and improving the overall business environment.
Market Creation: PPPs can create new markets and opportunities for private sector investment and innovation.
Challenges of PPPs
Complex Contractual ArrangementsNegotiation and Monitoring: PPP contracts are often complex, requiring extensive negotiation and continuous monitoring to ensure compliance and performance.
Dispute Resolution: Managing disputes between public and private partners can be challenging and may require robust legal frameworks and arbitration mechanisms.
Risk of Privatization of Public ServicesEquitable Access: There is a risk that the focus on profitability may lead to inequitable access to services, with the private sector prioritizing higher-paying customers.
Quality and Accountability: Ensuring that private partners maintain high-quality standards and accountability in service delivery can be difficult.
Financial RisksCost Overruns and Delays: PPP projects can face cost overruns and delays, impacting their financial viability and burdening public resources.
Long-Term Commitments: PPP agreements often involve long-term commitments, which can be challenging to manage, especially in the face of changing economic conditions and public priorities.
Capacity and ExpertiseGovernment Capacity: Effective implementation of PPPs requires significant capacity and expertise within government agencies to design, negotiate, and manage PPP contracts.
See less
Institutional Weaknesses: Inadequate institutional frameworks and weak regulatory environments can hinder the success of PPPs.
Conclusion
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as a crucial strategy for infrastructure development and public service delivery in India. The government’s efforts to promote PPPs through policy frameworks, financial incentives, and institutional support have yielded significant benefits, including enhanced efficiency, risk-sharing, and improved service quality. However, challenges such as complex contractual arrangements, risks of inequitable access, financial risks, and the need for robust government capacity must be addressed to maximize the potential of PPPs. Balancing the interests of public and private partners while ensuring equitable and high-quality service delivery remains key to the success of PPP initiatives.


Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of various processes, from diagnosis to treatment and patient care. Here are some key impacts of AI in healthcare: 1. Improved Diagnostics Medical Imaging: AI algorithms can analyze medical images sucRead more