Small businesses and startups can prioritize cybersecurity with limited resources by adopting several cost-effective strategies: Employee Training: Conduct regular cybersecurity training to educate employees on recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and following best practices for datRead more
Small businesses and startups can prioritize cybersecurity with limited resources by adopting several cost-effective strategies:
- Employee Training: Conduct regular cybersecurity training to educate employees on recognizing phishing emails, using strong passwords, and following best practices for data protection.
- Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement policies requiring strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable MFA to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all software, including operating systems, applications, and antivirus programs, are kept up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up data to secure, offsite locations. This ensures data can be restored in case of ransomware attacks or data loss.
- Firewall and Antivirus Protection: Install and maintain a reliable firewall and antivirus software to protect against malware and unauthorized access.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Use strong encryption for Wi-Fi networks and regularly change passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Limit Access: Implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring employees only have access to the data and systems necessary for their roles.
By focusing on these key areas, small businesses and startups can create a robust cybersecurity foundation without significant financial investment.
See less
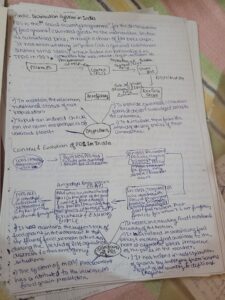
The Dravidian pattern of education also played a major role in the process of westernization of education in India especially during British rule. The Dravidian movement which was from South India was rationalism, self-respect and anti-caste movement which was in tune with a few of the Western educaRead more
The Dravidian pattern of education also played a major role in the process of westernization of education in India especially during British rule. The Dravidian movement which was from South India was rationalism, self-respect and anti-caste movement which was in tune with a few of the Western education systems.
Some of the leaders such as Periyar E. V. Ramasamy supported education to change scientific attitudes and secularism. This movement paved the way for the change in the education system from being dominated by the Brahmins and opened the doors of education to the downtrodden. The focus on rationalism and scientific method was in harmony with the Western educational models, which resulted in the assimilation of these features into the Indian educational system.
The change was also brought about by the Western missionaries and colonial administrators who introduced English education to the Indians which helped in the spread of Western scientific and rationalism. The Dravidian movement’s demand for educational changes supported these initiatives and created a secular and less prejudiced educational setting.
This combination of Dravidian rationalism with the Western education system helped in increasing the acceptance of Westernized education in India. It led to the formation of institutions that encouraged free thinking, scientific temper, and rationalism which are the basic foundations of modern India’s educational system which is a combination of Indian and Western systems.
See less