Examine how remote sensing and space-based Earth observation technology can help with global issues including climate change and resource management.
Model Answer Introduction Chandrayaan-3, launched by ISRO in 2023, represents India's third lunar mission. Unlike its predecessors, this mission includes a lander and a rover but no orbiter. The primary objective is to achieve a soft landing on the Moon's surface, a goal not accomplished in earlierRead more
Model Answer
Introduction
Chandrayaan-3, launched by ISRO in 2023, represents India’s third lunar mission. Unlike its predecessors, this mission includes a lander and a rover but no orbiter. The primary objective is to achieve a soft landing on the Moon’s surface, a goal not accomplished in earlier missions.
Main Task of Chandrayaan-3
Soft Landing
The mission’s core task is to execute a successful soft landing on the lunar surface. Chandrayaan-1 was solely an orbiter, while Chandrayaan-2 attempted a soft landing but failed due to a last-minute glitch. The successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 enables extensive lunar research and sample collection.
Lunar Research and Material Extraction
The successful landing allows scientists to analyze the Moon’s surface in detail, addressing limitations from previous missions. For instance, while Chandrayaan-1 identified water molecules, it couldn’t analyze samples. Chandrayaan-3 aims to collect lunar soil samples, a task that Chandrayaan-2 was unable to carry out due to its failed landing attempt.
Countries that Have Achieved Soft Landing
- USA: The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 achieved not just a soft landing but also human presence on the Moon (Source: NASA).
- Russia: Luna 9 marked the first successful soft landing in 1966, transmitting photographs back to Earth (Source: Soviet Space Program).
- China: Chang’e 3 achieved a soft landing in 2013, followed by Chang’e 4 landing on the far side of the Moon in 2019 (Source: China National Space Administration).
Subsystems in Chandrayaan-3
Vikram Lander
The Vikram lander is equipped with several advanced subsystems, including:
- Laser Inertial Referencing and Accelerometer Package (LIRAP)
- Ka-Band Altimeter (KaRA)
- Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera (LHDAC)
These systems work together to ensure a controlled descent and landing.
Pragyan Rover
The Pragyan rover is designed for surface exploration, conducting experiments and relaying data back to Earth.
Communication and Data Collection
The Deep Space Network ensures communication between the spacecraft and ground control, critical for mission success.
Role of the Virtual Launch Control Centre (VLCC)
The VLCC at Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre employs advanced technology to support the mission’s launch:
- Real-time Telemetry: Monitors all spacecraft subsystems during launch, ensuring functionality.
- Coordination: Synchronizes efforts across multiple systems and departments for a smooth launch.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies unexpected conditions during launch, providing data for quick decision-making.
- Resource Management: Enables experts to collaborate virtually, addressing complex challenges efficiently.
- Technological Advancements: Utilizes machine learning for real-time predictions and solutions, contributing significantly to the launch’s success.
Conclusion
The success of Chandrayaan-3 marks a significant milestone for India in space exploration, paving the way for future missions and enhancing India’s status in the global space community.
See less
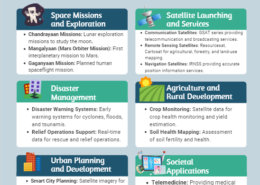
Space-based Earth observation and remote sensing technologies offer significant potential in addressing global challenges such as climate change and natural resource management. These technologies provide valuable data and insights that can inform policy decisions, enhance scientific understanding,Read more
Space-based Earth observation and remote sensing technologies offer significant potential in addressing global challenges such as climate change and natural resource management. These technologies provide valuable data and insights that can inform policy decisions, enhance scientific understanding, and support sustainable practices. Here’s an assessment of their potential impact:
**1. Climate Change Monitoring and Mitigation
**a. Tracking Climate Indicators
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**b. Disaster Management and Response
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**2. Natural Resource Management
**a. Water Resources
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**b. Agriculture and Land Use
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**3. Global Environmental Monitoring
**a. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**b. Air Quality Monitoring
Overview:
Potential Impact:
Examples:
**4. Challenges and Considerations
**a. Data Integration and Accessibility
Overview:
Challenges:
**b. Cost and Investment
Overview:
Challenges:
Conclusion
Space-based Earth observation and remote sensing technologies play a crucial role in addressing global challenges such as climate change and natural resource management. They provide valuable data for monitoring environmental changes, managing resources, and responding to natural disasters. While there are challenges related to data integration, accessibility, and costs, the potential benefits include enhanced scientific understanding, improved policy decisions, and better management of natural resources. To fully realize these benefits, continued investment in technology and international cooperation in data sharing and management are essential.
See less