How can the historical record of technological developments in ancient societies be found in pottery?
This infographic is a great introduction to the evolution of Indian pottery! The design is visually appealing and the information is presented in a clear and concise manner.
This infographic is a great introduction to the evolution of Indian pottery! The design is visually appealing and the information is presented in a clear and concise manner.
See less
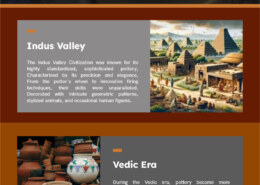
Pottery_TechAdvancement_Art&Culture Please find the answer in the attachment above.
Pottery_TechAdvancement_Art&Culture
Please find the answer in the attachment above.
See less