Talk about the difficulties in incorporating disaster risk reduction frameworks at the state and local levels in India with climate change adaptation initiatives.
According to WMO(World Meteorological Organization)- "Tsunami is a series of waves generated in a body of water by the displacement of large volume of water, usually as a result of earthquakes, landslides or volcanic eruptions". Formation of Tsunami - Displacement of water through earthquake, landslRead more
According to WMO(World Meteorological Organization)- “Tsunami is a series of waves generated in a body of water by the displacement of large volume of water, usually as a result of earthquakes, landslides or volcanic eruptions”.
Formation of Tsunami –
- Displacement of water through earthquake, landslides, volcanic eruptions or meteorites.
- Transfer of energy to the surrounding water.
- Wave formation and wave propagation at speed of upto 500 mph .
- Shoaling and amplification of waves led to pile up of water and increase in height near the coast.
- Tsunami waves reaches the coast causing widespread destruction and loss of life.
Tsunami preparedness involves –
- Preparedness and planning measures taken before a disaster strikes to minimize it’s impact ex-public education and mass awareness.
- Timely and accurate information to prevent and mitigate the impact of disasters.
- Emergency Response planning for unexpected events.
- Safe and orderly exit of the people.
- Recovery and rehabilitation efforts after the disaster.
- International cooperation for better management
- Technological Advancements enhance preparedness, response and recovery.
Mitigation Efforts taken by the governments –
- Creation of institutional framework like NDMA,INCOIS,IMD,NCMRWF.
- Coastal radar and surveillance system for early warning system.
- Tsunami resistant construction at Andaman and Nicobar islands .
- Regulatory measures like Disaster Management Act 2005 , Coastal Regulation Zone etc .
- Creation of Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC),Sendai framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2005 etc to promote international cooperation .
- Formation of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).

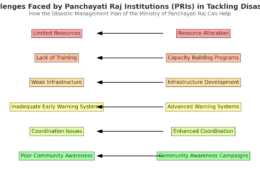

Integrating climate change adaptation strategies into disaster risk reduction (DRR) frameworks at the state and local levels in India presents several challenges. These challenges stem from the complexities of addressing both climate change and disaster risks, as well as the need for coordinated effRead more
Integrating climate change adaptation strategies into disaster risk reduction (DRR) frameworks at the state and local levels in India presents several challenges. These challenges stem from the complexities of addressing both climate change and disaster risks, as well as the need for coordinated efforts across various levels of governance and sectors. Here’s a discussion of the key challenges:
1. Institutional and Policy Fragmentation
2. Data and Information Gaps
3. Capacity Constraints
4. Community Engagement and Awareness
5. Policy and Regulatory Challenges
6. Financial and Economic Constraints
7. Implementation and Monitoring
Recommendations for Addressing Challenges:
In summary, integrating climate change adaptation strategies into disaster risk reduction frameworks at the state and local levels in India involves addressing challenges related to institutional coordination, data availability, capacity, community engagement, policy alignment, financial constraints, and implementation. By addressing these challenges and implementing targeted recommendations, India can enhance its preparedness and resilience to both climate change and natural disasters.
See less