Roadmap for Answer Writing 1. Introduction Context: Introduce the issue of increasing incidents of cloudbursts in Uttarakhand and their impact on life and property. Thesis Statement: Highlight the relevance of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines in mitigating these impacts. 2. NDMA Guidelines ...
The Bhopal Gas tragedy of 1984 is the amongst the worst chemical disaster in history, where over 2000 people died due to the accidental release of the toxic gas Methyl Isocyanate. Recently, the Vizag gas leak at LG Polymers plant in Visakhapatnam killed 12 people and sickened hundreds. Chemical disaRead more
The Bhopal Gas tragedy of 1984 is the amongst the worst chemical disaster in history, where over 2000 people died due to the accidental release of the toxic gas Methyl Isocyanate. Recently, the Vizag gas leak at LG Polymers plant in Visakhapatnam killed 12 people and sickened hundreds. Chemical disasters, though low in frequency, have the potential to cause significant immediate or long-term damage, like injuries, permanent disabilities, loss of lives, damage to property and environment. India is amongst the very few countries, which have enshrined the right to live in a clean and wholesome environment as a fundamental right. After the Bhopal disaster in 1984, Chemical Disaster Management (CDM) received greater emphasis and following steps have been taken to prepare the mechanism to deal with any such disaster:
- Regulatory framework: There are various legislations, which take into account CDM. For, example, Indian factories Act, 1948, The Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules 1989, The Chemical Weapons Convention Act 2000, CAEPPR Rules 1996, Public Liability Insurance Act 1991, Explosives Act-1884, Insecticide Act-1968, Environment (Protection) Act-1986, and Disaster Management (DM) Act-2005. These regulatory frameworks deal with various issues like working conditions, regulating the usage of chemicals, mitigation efforts etc.
- Institutional framework: A separate Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), has been earmarked as the nodal ministry for management of chemical disasters to ease coordination amongst other ministries, institutions and agencies to manage these disasters. Besides, research institutes like IITs, NEERI, etc. are also working in this domain.
- NDMA guidelines to ministries/departments and states for preparing DM plans: The guidelines focus on all aspects of the DM cycle including prevention, mitigation, preparedness, relief, rehabilitation and recovery.
- Other technical efforts: Installation of major accident Hazard Control System, GIS-based Emergency Management System, Environment Risk Reporting and Information Systems (ERRIS), etc.
- Capacity building: Financial assistance has been provided for capacity development in CDM to various disaster management training institutes.
While considerable progress has been made in the management of chemical disasters, critical gaps still exist in certain areas
- Complex web of laws: Regulatory frameworks have numerous laws for various aspects under different ministries thus making it more difficult in terms of synchronizing the policies and have various issues at implementation levels and making it even more difficult for regulations.
- Gaps in codes of practices, procedures and standards: There is a lack of national level risk assessment criteria and acceptable risks for chemical plants. Also, there are lacunae in procedure for conduct of safety audit and departmental inspections.
- Untrained professionals: There is a lack of knowledge amongst the government officials, medical staff, as well as staff of the industry on CDM. Also, there is a shortage of clear accessible information on potential chemical hazards and their management.
- Infrastructural gaps: Institutional framework for providing technical support at various levels is a key requirement for sustaining proper development and implementation of an effective disaster management system. These have not been fully identified.
- Gaps in post disaster management: Mechanisms to deal with social and economic impacts of chemicals on human health, society and the environment, including liability, compensation and redress are not streamlined and strengthened to take adequate care of post disaster mitigation.
Although good efforts have been made to minimize such accidents and to improve emergency preparedness at all levels, more needs to be done. One step in this regard can be preparing a database of all potential chemicals used in industries. Substantial efforts are still required to predict the potential occurrence of disasters, assess the damage potential, issue warnings, and to take other precautionary measures to mitigate their effects.
See less
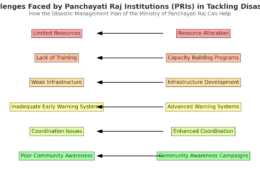

Model Answer Introduction Uttarakhand, a state in northern India, has faced numerous incidents of cloudbursts recently, leading to significant loss of life and property. To effectively mitigate the impact of these natural disasters, the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has formulated coRead more
Model Answer
Introduction
Uttarakhand, a state in northern India, has faced numerous incidents of cloudbursts recently, leading to significant loss of life and property. To effectively mitigate the impact of these natural disasters, the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has formulated comprehensive guidelines.
Mitigating Cloudburst Impact in Uttarakhand: NDMA Guideline-Based Measures
Conclusion
By implementing these NDMA guidelines, Uttarakhand can strengthen its disaster management strategies and minimize the impact of cloudburst incidents. Timely preventive measures, early warning systems, and community participation will significantly reduce casualties and enhance resilience in affected regions.
See less