It’s time to describe how novel technologies such as blockchain solutions enhance the credibility of carbon trading and offset markets. What potential issues do we encounter when using blockchain for climate programs?
Blockchain technology's decentralized nature is revolutionizing cybersecurity in several key ways: 1. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain operates as a distributed ledger, meaning that data is stored across a network of computers (nodes) rather than a single central server. This makes it much moreRead more
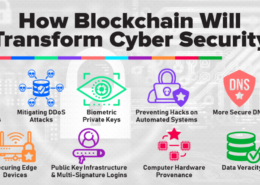
Blockchain technology’s decentralized nature is revolutionizing cybersecurity in several key ways:
1. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain operates as a distributed ledger, meaning that data is stored across a network of computers (nodes) rather than a single central server. This makes it much more difficult for hackers to attack because there is no single point of failure. Compromising the network would require simultaneously attacking a majority of the nodes.
2. Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it is extremely difficult to alter. This immutability helps prevent unauthorized changes and tampering. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain of information.
3. Transparency and Traceability: Transactions on a blockchain are transparent and can be traced back to their origin. This transparency deters fraudulent activities and enhances trust, as all participants can see the same information and verify it independently.
4. Decentralized Consensus: Blockchain uses consensus mechanisms (such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to validate transactions. This means that no single entity controls the verification process, reducing the risk of corruption or manipulation.
5. Enhanced Security Protocols: Blockchain technology employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Public and private keys, along with digital signatures, ensure that only authorized users can access and execute transactions.
6. Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute agreements when predetermined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and enhancing security through automation.
By decentralizing data storage and verification, blockchain technology significantly enhances cybersecurity, making systems more resilient to attacks, reducing fraud, and increasing trust among users.
See less
Blockchain technology enhances the credibility of carbon trading and offset markets by: *Benefits:* 1. Transparency: Immutable ledger ensures tamper-proof data. 2. Traceability: End-to-end tracking of carbon credits. 3. Verification: Smart contracts validate emission reductions. 4. Security: CryptogRead more
Blockchain technology enhances the credibility of carbon trading and offset markets by:
*Benefits:*
1. Transparency: Immutable ledger ensures tamper-proof data.
2. Traceability: End-to-end tracking of carbon credits.
3. Verification: Smart contracts validate emission reductions.
4. Security: Cryptographic encryption safeguards transactions.
5. Efficiency: Automated processes reduce administrative costs.
*Blockchain-based Carbon Trading Platforms:*
1. Veridium (tokenized carbon credits)
2. CarbonX (blockchain-based carbon offsetting)
3. ClimateTrade (decentralized carbon marketplace)
4. Gold Standard (blockchain-verified emission reductions)
*Potential Issues:*
1. Scalability: Limited transaction capacity.
2. Energy Consumption: Blockchain’s high energy footprint.
3. Regulatory Frameworks: Lack of clear guidelines.
4. Data Quality: Ensuring accurate emission data.
5. Interoperability: Integration with existing systems.
6. Market Volatility: Price fluctuations in carbon credits.
7. Double Counting: Preventing duplicate emission reductions.
8. Security Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
*Mitigating Potential Issues:*
1. Layer 2 scaling solutions (e.g., Polygon).
2. Energy-efficient consensus algorithms (e.g., Proof of Stake).
3. Collaborative regulation (e.g., ICAP).
4. Data validation through IoT sensors.
5. Standardized data formats.
6. Market stabilization mechanisms.
7. Unique identifiers for emission reductions.
8. Regular security audits.
*Future Directions:*
1. Integration with IoT devices.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for data analysis.
3. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
4. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for carbon credits.
5. Blockchain-based climate governance.
By addressing potential issues and leveraging blockchain’s benefits, we can create a more transparent, efficient, and credible carbon trading and offset market, ultimately supporting global climate goals.
See less