What is password salting? Why is it considered a safer alternative for encryption of passwords?
**How Encryption Works to Secure Data:** Encryption transforms readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and a key. Only authorized parties with the correct decryption key can revert the ciphertext back to plaintext, ensuring data confidentiality. EncryptionRead more
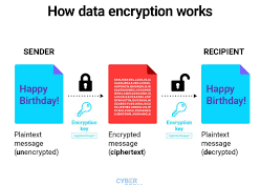
**How Encryption Works to Secure Data:**
Encryption transforms readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and a key. Only authorized parties with the correct decryption key can revert the ciphertext back to plaintext, ensuring data confidentiality. Encryption secures data during storage (at rest) and transmission (in transit), protecting it from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
**Types of Encryption Methods in Cybersecurity:**
1. **Symmetric Encryption:**
– Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption.
– Fast and efficient, suitable for encrypting large volumes of data.
– Common algorithms: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard).
2. **Asymmetric Encryption:**
– Utilizes a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
– Provides stronger security but is slower than symmetric encryption.
– Common algorithms: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography).
3. **Hash Functions:**
– Converts data into a fixed-size hash value, which is unique to the original data.
– Primarily used for data integrity and verification, not reversible.
– Common algorithms: SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm), MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5).
4. **Hybrid Encryption:**
– Combines symmetric and asymmetric encryption to leverage the strengths of both methods.
– Typically uses asymmetric encryption to securely exchange the symmetric key.
– Commonly used in protocols like SSL/TLS for secure web communications.
These encryption methods are fundamental to cybersecurity, ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity across various applications and platforms.
See less
Password Salting: Password salting is a security practice that involves adding a unique, random value (known as a "salt") to each password before hashing it. This salt value is stored along with the hashed password in the database. When a user logs in, the system retrieves the salt, appends it to thRead more
Password Salting:
Password salting is a security practice that involves adding a unique, random value (known as a “salt”) to each password before hashing it. This salt value is stored along with the hashed password in the database. When a user logs in, the system retrieves the salt, appends it to the entered password, and hashes the combination to verify against the stored hash.
Why It Is Safer:
- Prevents Hash Collisions:
- Adding a unique salt ensures that even identical passwords result in different hashes, preventing attackers from identifying common passwords across multiple accounts.
- Mitigates Precomputed Attacks:
- Salting effectively thwarts precomputed attacks such as rainbow table attacks, where attackers use precompiled lists of hash values for common passwords. Since each salt is unique, attackers cannot use these tables effectively.
- Increases Brute Force Complexity:
- With unique salts, attackers must brute-force each password individually rather than using a single effort for multiple accounts, significantly increasing the time and computational resources required for a successful attack.
- Reduces Impact of Data Breaches:
- Even if an attacker gains access to the hashed passwords and their corresponding salts, the complexity added by the salts makes it much harder to reverse-engineer the original passwords.
See less