Examine the effects of the growing wealth and income gaps in India and evaluate the government’s attempts to address these issues with focused initiatives like the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana.
"It is a regret that Article 44 has remained a dead letter" said Justice Y V Chandrachud in Shah Bano judgement (1985). Our constitution-makers have placed 'Uniform Civil Code(Article 44)' under Directive principles of State Policy(Part IV). Need for UCC to balance diversity and ensure social justiRead more
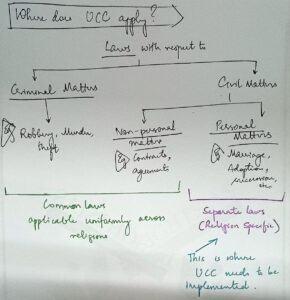
“It is a regret that Article 44 has remained a dead letter” said Justice Y V Chandrachud in Shah Bano judgement (1985). Our constitution-makers have placed ‘Uniform Civil Code(Article 44)’ under Directive principles of State Policy(Part IV).
Need for UCC to balance diversity and ensure social justice
1) It enhances ‘Secularism’ – mentioned in Preamble and a part of Basic structure.
2) It is based on ‘Equality’ – a fundamental right (Article 14)
3) Personal laws are usually against women and marginal, vulnerable sections.
For example, Shariat – allows polygamy (Sarala Mudgal Case)
5) States like Goa, Uttarkhand have adopted UCC after legislative consensus
6) Supreme Court has supported its implementation in multiple instances.
Challenges to implement UCC
1. Article 26 provides for the right to manage one’s own religious matters.
2. Debate of – Fundamental Rights(Article 26) v/s DPSPs(Article 44)
3. STs have customary laws protected by the constitution itself.
4. Apprehensions of imposition of majoritarian values on minority
5. Accommodating diversity
Way forward
1) 22nd Law commission sought public consultation process on UCC
2) Consensus building that UCC is necessary
3) In the short-term personal laws can be codified phase-wise
4) UCC should not be imposed right away through an ordinance, it should pass through parliamentary debates and deliberations
5) Political parties should rise above differences for the common good of all
A fundamental change in people’s mindset is required for UCC’s implementation.
See less
Implications of Rising Income Inequality and Wealth Disparity in India 1. Current Trends in Income Inequality and Wealth Disparity Rising Income Inequality Statistics: Income inequality in India has been increasing. According to the World Inequality Report 2022, the top 1% of earners in India controRead more
Implications of Rising Income Inequality and Wealth Disparity in India
1. Current Trends in Income Inequality and Wealth Disparity
Rising Income Inequality
Wealth Disparity
Implications of Rising Inequality
Economic Impact
Social Impact
2. Government Efforts to Address Inequality
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
Objective and Achievements
Impact
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Objective and Achievements
Impact
3. Challenges and Limitations
PMJDY
GST
4. Recommendations for Improvement
Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Reforming GST
5. Conclusion
Rising income inequality and wealth disparity in India have significant economic and social implications, affecting consumption patterns, social stability, and overall economic growth. The government’s efforts through initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and the Goods and Services Tax aim to address these challenges by improving financial inclusion and creating a more equitable tax system. However, challenges remain in the implementation and effectiveness of these programs. Addressing these issues through targeted reforms and enhanced support can help in better achieving the goal of reducing inequality and promoting inclusive growth.
See less