What does the term “public debt” mean to you? Why is a high level of national debt seen as concerning? Talk about it in relation to India. (Answer in 200 words)
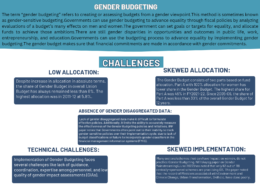
Model Answer 1. Increased Financial Allocation The budget allocates ₹2.23 lakh crore for women-centric projects, marking a 2.12% increase from the previous year and a 30% rise compared to last year's Budget Estimates of ₹1.71 lakh crore. This substantial financial commitment underscores the governmeRead more
Model Answer
1. Increased Financial Allocation
The budget allocates ₹2.23 lakh crore for women-centric projects, marking a 2.12% increase from the previous year and a 30% rise compared to last year’s Budget Estimates of ₹1.71 lakh crore. This substantial financial commitment underscores the government’s focus on women’s empowerment as a key development agenda.
2. Enhancing Women’s Safety
A notable increase in funding for the ‘Safe City Project’ from ₹165 crores in 2022-23 to ₹1,300 crores in 2023-24 aims to improve safety for women in public spaces. This enhancement is crucial for encouraging women’s participation in economic activities and increasing the overall labor force participation rate.
3. Strengthening Property Rights
The budget also boosts the allocation for the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana by 66% to ₹79,000 crore, which will strengthen women’s property entitlements. Additionally, the introduction of differential tax rates for property registration is expected to improve women’s access to land and property, further empowering them economically.
4. Promoting Financial Independence
The Mahila Samman Savings Certificate scheme, offering up to ₹2 lakh for a two-year period at a fixed interest rate of 7.5%, is designed to foster financial independence among women. This initiative encourages savings and provides flexibility for partial withdrawals, which can be utilized for education and health needs.
5. Support for Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
The budget prioritizes the development of women-led self-help groups by providing them with essential resources such as raw materials, branding, and marketing support. This initiative aims to enhance rural income and promote financial independence among women.
6. Health and Well-being Initiatives
Increased funding for health-related schemes like Saksham Anganwadi, Poshan 2.0, and Mission Shakti will improve the quality of services available to women, particularly in areas such as sexual and reproductive healthcare and child health.
Conclusion
To maximize the impact of these initiatives, it is essential to establish a robust monitoring system to assess the effectiveness of budgetary allocations. Transparent auditing mechanisms should be implemented to enhance women’s participation in economic activities and improve their overall well-being. Each Ministry and Department should also develop a roadmap to address specific structural barriers faced by women, ensuring the effective utilization of funds aimed at achieving gender equality.
See less

Public debt, also known as government debt or national debt, refers to the total amount of money owed by a country's government to its citizens, businesses, and foreign investors. It is a cumulative result of budget deficits, borrowing for various purposes, and interest payments. High public debt isRead more
Public debt, also known as government debt or national debt, refers to the total amount of money owed by a country’s government to its citizens, businesses, and foreign investors. It is a cumulative result of budget deficits, borrowing for various purposes, and interest payments.
High public debt is a matter of concern for several reasons:
1. Burden on future generations: High debt may lead to increased taxation and reduced government spending on essential services, affecting future generations.
2. Inflation: Excessive borrowing can lead to inflation, reducing the purchasing power of citizens.
3. Reduced credit rating: High debt may lower a country’s credit rating, increasing borrowing costs and reducing investor confidence.
4. Reduced fiscal space: High debt limits a government’s ability to respond to economic downturns or fund development projects.
In the context of India, high public debt is a concern due to:
– Rising debt to GDP ratio (currently over 90%)
– Large fiscal deficits
– Increasing reliance on market borrowing
– Pressure on interest payments (around 50% of tax revenue)
– Limited fiscal space for development spending
To address these concerns, India needs to focus on fiscal consolidation, improve tax compliance, and enhance economic growth through structural reforms.
See less