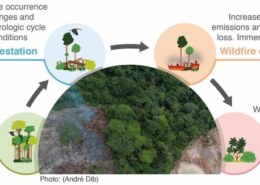
Deforestation occurs when forests are converted to non-forest uses, such as agriculture and road construction. It leads to the long-term loss of forest area. In contrast, forest degradation doesn’t reduce the forest area but rather results in a qualitative decline in forest condition. Forest ecosystRead more
Deforestation occurs when forests are converted to non-forest uses, such as agriculture and road construction. It leads to the long-term loss of forest area. In contrast, forest degradation doesn’t reduce the forest area but rather results in a qualitative decline in forest condition. Forest ecosystems lose their capacity to provide essential goods and services to people and nature during degradation. These threats jeopardize the critical role forests play in purifying water, mitigating climate change, and supporting biodiversity.
Local Impacts:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Deforestation disrupts habitats, leading to the loss of plant and animal species. Many species rely on specific forest ecosystems for survival.
- Changes in Water Cycle: Healthy forests play a vital role in the local water cycle by creating rainfall. When deforestation occurs, forests are less capable of fulfilling this role, resulting in changes in precipitation and river flow1.
- Soil Erosion: Tree roots stabilize soil, preventing erosion. Without trees, soil becomes vulnerable to erosion, affecting local agriculture and water quality.
- Temperature and Rainfall Changes: Deforestation, especially in tropical regions, impacts local temperatures and rainfall. These changes can compound the effects of global climate change, affecting human health and agricultural productivity.
Global Impacts
- Climate Change: Almost 17.4% of global greenhouse gas emissions result from deforestation and forest degradation. Trees store carbon, and excessive deforestation releases this carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
- Carbon Sink Loss: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide. Deforestation reduces this capacity, exacerbating climate change.
- Altered Weather Patterns: Deforestation affects weather patterns globally, impacting rainfall distribution and temperature regulation.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Forests provide essential services like air and water purification, nutrient cycling, and pollination. Their loss affects global ecosystems and human well-being.
Governments can provide policies and regulations that promote sustainable forestry practices and penalize companies that engage in deforestation.Efforts to combat deforestation include responsible forest management, reforestation, and sustainable land use practices. Protecting forests is crucial for a healthy planet and the well-being of all living beings.
See less
Reasons for the Rise of the Roman Empire: 1. Military Conquests: Successful military campaigns expanded territory and influence, securing resources and wealth. 2. Strategic Alliances: Diplomatic alliances with neighboring states and tribes bolstered Rome's power and stability. 3. Administrative EffiRead more
Reasons for the Rise of the Roman Empire:
1. Military Conquests: Successful military campaigns expanded territory and influence, securing resources and wealth.
2. Strategic Alliances: Diplomatic alliances with neighboring states and tribes bolstered Rome’s power and stability.
3. Administrative Efficiency: Effective governance and legal reforms facilitated centralized control and integration of conquered regions.
4. Economic Prosperity: Trade, agriculture, and taxation generated significant wealth, supporting infrastructure and public projects.
5. Cultural Integration: Assimilation of diverse cultures and practices strengthened societal cohesion and loyalty.
Reasons for the Fall of the Roman Empire:
1. Political Corruption: Ineffective leadership and corruption weakened governance and administration.
See less2. Economic Decline: Heavy taxation, inflation, and economic mismanagement eroded financial stability.
3. Military Overreach: Overexpansion led to logistical challenges and vulnerability to external invasions.
4. Barbarian Invasions: Continuous invasions by barbarian tribes destabilized the Empire’s borders.
5. Internal Conflict: Civil wars and power struggles undermined unity and cohesion.