What Is the Internet of Things? How Does IoT Work?
Resources & Suggestions
Mains Answer Writing Latest Articles
Daily Answer Writing Practice Questions (18 April 2025)
Do you agree with the claim that indecision and risk aversion are prevalent issues in Indian bureaucracy? Support your answer with logical reasoning. (150 words) ऐसा कहा जाता है कि भारतीय नौकरशाही में अनिर्णय और जोखिम से बचने की प्रवृत्ति ...
Strengthening India’s Cyber Defence
Rising Threats Digital Era Challenges: 2024 marks a significant rise in digital threats, particularly from AI and cyberattacks. Key Issues: Disinformation campaigns. Cyber fraud affecting daily life. Current Major Cyber Threats Ransomware Rampage: Over 48,000 instances of WannaCry ransomware detected ...
भारत की साइबर सुरक्षा
बढ़ते खतरे कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (AI) और साइबर हमले: 2024 में AI और साइबर हमलों के खतरे में वृद्धि। महत्वपूर्ण अवसंरचना पर हमले: डिजिटल हमलों और दुष्प्रचार अभियानों की संभावना बढ़ी है। प्रमुख साइबर खतरें रैनसमवेयर का प्रकोप: 48,000 से अधिक ...

The Internet of Things (IoT) impacts our daily lives by connecting everyday devices to the internet, enabling them to communicate and work together. For example, in smart homes, you can control lights, thermostats, and security cameras through your phone, making life more convenient and efficient. Wearable devices like fitness trackers monitor your health and activity levels, providing useful data to help you stay fit. In cities, IoT helps manage traffic, monitor air quality, and optimize waste collection, making urban living more comfortable and sustainable. IoT makes life easier and smarter through connected technology.
The Internet of Things (IoT) integrates everyday objects with the internet, enabling them to send and receive data. IoT devices are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity to perform specific tasks, communicate with each other, and interact with users.
Real-life IoT examples:
IoT’s pervasive integration in various sectors enhances efficiency, safety, and user convenience.
IoT (Internet of Things) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
Here are some real-life IoT examples:
1. *Smart Home Appliances*: Wi-Fi enabled thermostats, like Nest, can learn your temperature preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly.
2. *Wearables*: Fitness trackers, like Fitbit, can monitor your heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns, providing valuable health insights.
3. *Industrial Automation*: IoT sensors in manufacturing plants can monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
4. *Smart Cities*: IoT sensors in traffic management systems can optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving public safety.
5. *Agriculture*: IoT sensors in soil can monitor moisture levels, temperature, and crop health, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions.
6. *Healthcare*: IoT devices, like pacemakers and insulin pumps, can monitor patients’ vital signs and deliver personalized treatment.
7. *Transportation*: IoT sensors in vehicles can monitor performance, navigation, and safety features, enabling advanced driver-assistance systems.
These examples illustrate how IoT technology integrates physical devices with digital intelligence, enhancing efficiency, convenience, and decision-making in various aspects of life.
IoT (Internet of Things) works by connecting physical devices, sensors, and actuators to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data, and interact with the physical world. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
1. *Device Connection*: Devices like sensors, actuators, and smart appliances connect to the internet through various networks (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE, etc.).
2. *Data Collection*: Devices collect data from their surroundings, such as temperature, humidity, motion, or light.
3. *Data Transmission*: Devices send the collected data to the cloud, gateways, or other devices through the internet.
4. *Data Processing*: The received data is processed and analyzed in the cloud or on local devices using various algorithms and AI models.
5. ** Insights and Actions**: The processed data provides valuable insights, triggering actions like sending notifications, controlling devices, or automating processes.
Here are some real-life IoT examples:
– *Smart Thermostats*: Learn your temperature preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly.
– *Industrial Automation*: Monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
– *Wearables*: Track fitness goals, monitor health metrics, and receive personalized recommendations.
– *Smart Home Security*: Detect intrusions, alert homeowners, and notify authorities.
– *Agricultural Sensors*: Monitor soil moisture, temperature, and crop health, enabling data-driven farming decisions.
– *Smart Cities*: Optimize traffic flow, waste management, and public safety using IoT sensors and data analytics.
These examples demonstrate how IoT integrates physical devices with digital intelligence, enhancing efficiency, convenience, and decision-making in various aspects of life.
The Internet of Things (IoT) works by connecting various devices to the internet, enabling them to collect, exchange, and act on data. IoT systems typically consist of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces.
How IoT Works:
Flow Chart:
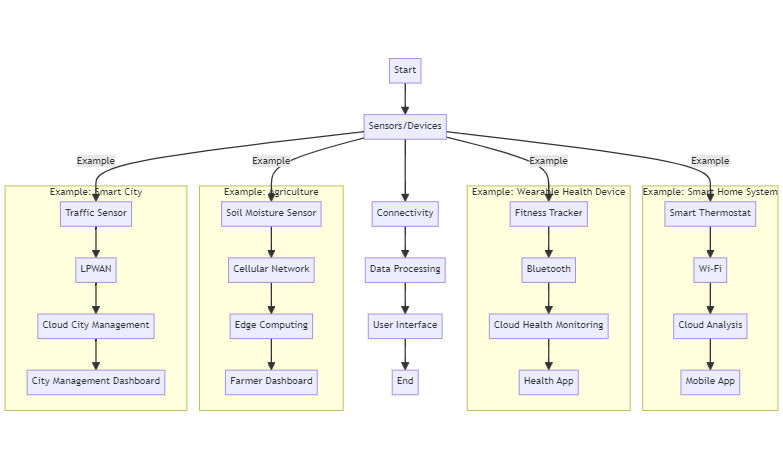
Real-Life IoT Examples:
By leveraging IoT technology, various industries can enhance operational efficiency, improve decision-making, and offer innovative services to users.