Identify the key variables affecting India’s inflation rate.
Inflation targeting is a monetary policy framework where a central bank sets a specific inflation rate as its target and uses monetary policy tools to achieve and maintain price stability. In India, the inflation targeting framework was adopted in 2016, and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is responsRead more
Inflation targeting is a monetary policy framework where a central bank sets a specific inflation rate as its target and uses monetary policy tools to achieve and maintain price stability. In India, the inflation targeting framework was adopted in 2016, and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is responsible for its implementation.
Here’s how it operates in India:
1. Target: The RBI sets an inflation target of 4% with a tolerance band of +/- 2% (i.e., 2-6%).
2. Framework: The RBI uses a flexible inflation targeting framework, which means it considers growth and other macroeconomic factors while setting policy rates.
3. Tools: The RBI uses monetary policy tools like the repo rate (short-term lending rate), reverse repo rate, and open market operations to manage liquidity and inflation.
4. Decision-making: The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meets every two months to review inflation trends, growth, and other factors to decide on policy rates.
5. Communication: The RBI communicates its inflation projections and policy decisions to the public, ensuring transparency and accountability.
By adopting an inflation targeting framework, India aims to maintain price stability, promote economic growth, and enhance the credibility of monetary policy.
See less
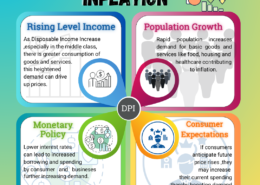
Inflation Factors in India Inflation in India is a complex issue influenced by various factors, ranging from global economic trends to domestic policies. This timeline explores some of the major contributors to inflation in the country. 2021-2023 Global Commodity Prices The surge in glRead more
Inflation Factors in India
Inflation in India is a complex issue influenced by various factors, ranging from global economic trends to domestic policies. This timeline explores some of the major contributors to inflation in the country.
2021-2023
Global Commodity Prices
The surge in global commodity prices, particularly oil and food, due to supply chain: disruption and increased demand contributed significantly to India’s inflation.
2021-2022
Fuel Price Hike
Rising Fuel prices, driven by Increased global oil prices and domestic taxes, impacted transportation cost, leading to inflation in various sectors.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains , leading to shortages and price increases for various goods, contributing to inflation.
2022-23
Weak Rupee
A weakening rupees against the US dollar increased the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices and contributing to inflation.
2022-23
Monetary Policy
The Reserve Bank of India’s monetary Policy, including interest rates adjustment, influenced inflation by implementing borrowing costs and consumer spending.
See less