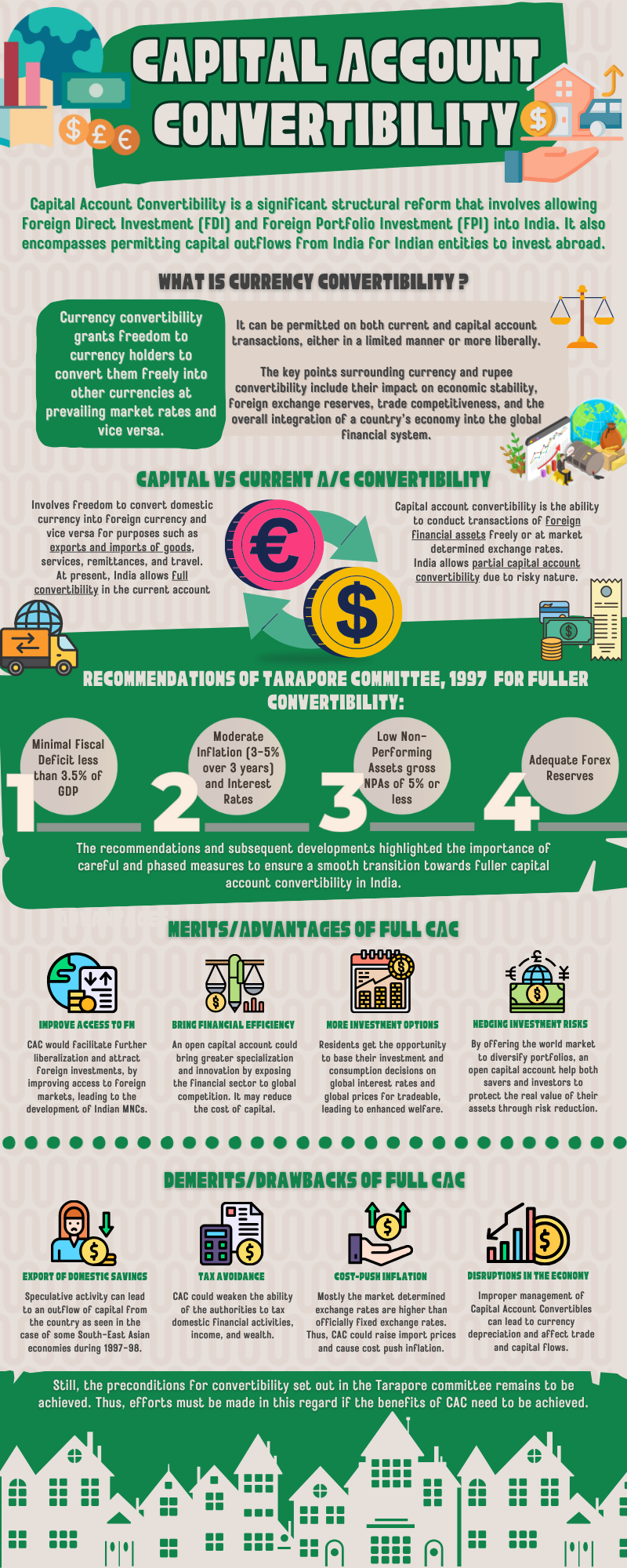
Examine how India’s external sector has been affected by disruptions to the global supply chain, changes in trade and investment patterns, and the emergence of geopolitical dynamics. Also, evaluate the measures the nation has taken to strengthen its resilience and ...
Factors Contributing to the Widening of India's Current Account Deficit 1. Rising Cost of Oil Imports: Dependence on Oil Imports: India is heavily reliant on oil imports to meet its energy needs. As of recent data, oil imports constitute a significant portion of India's total import bill. The globalRead more
Factors Contributing to the Widening of India’s Current Account Deficit
1. Rising Cost of Oil Imports:
- Dependence on Oil Imports: India is heavily reliant on oil imports to meet its energy needs. As of recent data, oil imports constitute a significant portion of India’s total import bill. The global oil market’s volatility impacts India directly, leading to an increase in the cost of imports.
- Impact of Global Oil Prices: In 2023, global oil prices surged due to geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, exacerbating India’s import bill. For example, the crude oil prices saw a substantial rise in mid-2023 due to OPEC+ production cuts and conflicts in oil-producing regions.
2. Volatility in Commodity Prices:
- Fluctuations in Global Commodity Markets: The prices of commodities like metals, minerals, and agricultural products are highly volatile. In 2024, the prices of essential commodities like copper and steel have experienced sharp fluctuations due to supply chain issues and geopolitical uncertainties.
- Impact on Import Costs: India imports a significant amount of raw materials and commodities. The volatility in prices increases the cost of these imports, contributing to a higher current account deficit.
3. Trends in Invisible Trade (Services and Remittances):
- Services Export Growth: India’s service sector, particularly IT and business process outsourcing (BPO), has been a strong contributor to invisible trade. However, recent trends show a slowdown in global demand for Indian IT services due to increasing competition and economic uncertainties in key markets like the US and Europe.
- Remittances: While remittances from the Indian diaspora are a critical source of foreign exchange, their growth has been uneven. In 2024, despite robust remittances, their impact has been offset by the growing import bill and other economic factors.
Government Efforts to Address External Sector Imbalances
1. Strengthening Trade Policy:
- Import Substitution Policies: The Indian government has promoted policies aimed at reducing dependency on imports by boosting domestic production through initiatives like “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (Self-Reliant India). This includes encouraging local manufacturing and reducing the reliance on imported raw materials.
- Trade Agreements: India has been actively pursuing bilateral and multilateral trade agreements to open up new markets for its exports. For instance, recent trade agreements with the UAE and Australia aim to enhance India’s export opportunities and improve the trade balance.
2. Managing Oil Price Volatility:
- Strategic Reserves: The Indian government has increased efforts to build strategic petroleum reserves to mitigate the impact of sudden oil price spikes. This is intended to provide a buffer against short-term supply disruptions and price volatility.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Initiatives to diversify energy sources, including investments in renewable energy and exploring alternative energy supplies, are ongoing to reduce reliance on oil imports.
3. Enhancing Foreign Exchange Reserves:
- Foreign Investment: The government has taken steps to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment to bolster foreign exchange reserves. Measures such as easing FDI norms and improving the investment climate are part of this strategy.
- Reserve Management: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively manages the country’s foreign exchange reserves to stabilize the currency and mitigate the impact of external shocks.
Conclusion
The widening of India’s current account deficit is influenced by multiple factors, including the rising cost of oil imports, volatility in commodity prices, and trends in invisible trade. The Indian government has undertaken several measures to address these external sector imbalances, such as enhancing trade policies, managing oil price volatility, and strengthening foreign exchange reserves. While these efforts are crucial, continued vigilance and adaptation are necessary to navigate the challenges posed by global economic uncertainties.
See less
Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions, Shifts in Trade Patterns, and Geopolitical Dynamics on India's External Sector 1. Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Disruptions Due to COVID-19 and Beyond: The COVID-19 pandemic triggered severe disruptions in global supply chains, affecting India’Read more
Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions, Shifts in Trade Patterns, and Geopolitical Dynamics on India’s External Sector
1. Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions:
2. Shift in International Trade and Investment Patterns:
3. Emerging Geopolitical Dynamics:
Assessment of India’s Strategies to Enhance Resilience and Adaptability
1. Strengthening Domestic Manufacturing Capabilities:
2. Diversification of Trade and Investment Partners:
3. Enhancing Geopolitical and Strategic Alliances:
Conclusion
The impact of global supply chain disruptions, shifts in international trade and investment patterns, and emerging geopolitical dynamics on India’s external sector has been significant. India’s strategies to enhance resilience and adaptability include strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities, diversifying trade and investment partners, and reinforcing geopolitical alliances. These measures aim to mitigate external vulnerabilities and capitalize on new opportunities in a rapidly changing global landscape.
See less