Waterfall Methodology: Sequential Process: Waterfall is a linear and sequential approach. Each phase must be completed before the next one begins. Stages: Typical stages include Requirements, Design, Implementation, Testing, and Maintenance. Example: Building a house. You complete the foundation befRead more
Waterfall Methodology:
- Sequential Process: Waterfall is a linear and sequential approach. Each phase must be completed before the next one begins.
- Stages: Typical stages include Requirements, Design, Implementation, Testing, and Maintenance.
- Example: Building a house. You complete the foundation before starting the walls, then the roof, and so on. You can’t go back to change the foundation once the walls are up.
Agile Methodology:
- Iterative Process: Agile is iterative and flexible. Work is divided into small chunks called sprints, usually lasting 2-4 weeks.
- Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback and adjustments are made throughout the project.
- Example: Developing a mobile app. You create a basic version with core features, get feedback, and then add more features and improvements in subsequent sprints. You can make changes at any point based on feedback.
Here are the differences between Agile and Waterfall methodologies in simple terms: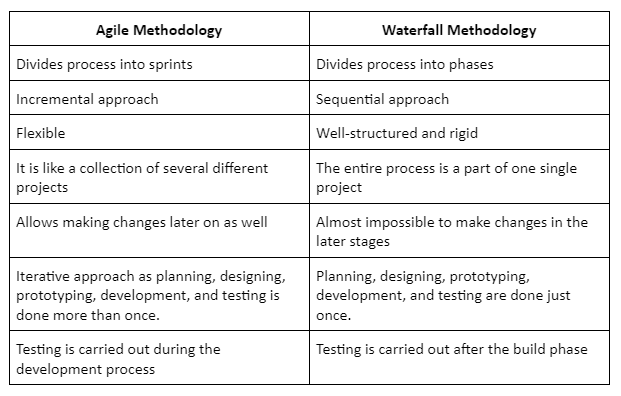

Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development approach where you write tests for your code before you actually write the code itself. This helps ensure that your code works correctly from the very beginning. Here's how it works in simple steps: Let's say you're building a simple calculatorRead more
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development approach where you write tests for your code before you actually write the code itself. This helps ensure that your code works correctly from the very beginning. Here’s how it works in simple steps:
Let’s say you’re building a simple calculator that can add two numbers.
1,Write a Test: First, you write a test to check if the
addfunction works.This test checks if adding 2 and 3 gives you 5. Since you haven’t written the
addfunction yet, this test will fail.2.Write the Code: Now, you write the
addfunction to pass the test.3.Run the Test: Run the test to see if it passes.
4.Repeat: Next, you could write a test for another function, like subtraction, and go through the same steps.This cycle helps ensure your code works correctly and makes it easier to find and fix bugs early in the development process.
Test-driven development (TDD) benefits include better code quality, clear documentation, confident refactoring, faster debugging, modular development, improved design, stakeholder confidence, team collaboration, predictability, regression prevention, easier onboarding, and long-term cost savings.
I’m glad you found it useful! If you have any more questions or need further clarification on any topic, feel free to ask.
See less