What are the benefits and challenges of using drones and IoT devices in modern agriculture?
The Internet of Things (IoT) works by connecting various devices to the internet, enabling them to collect, exchange, and act on data. IoT systems typically consist of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces. How IoT Works: Sensors/Devices: Collect data from their environment (e.Read more
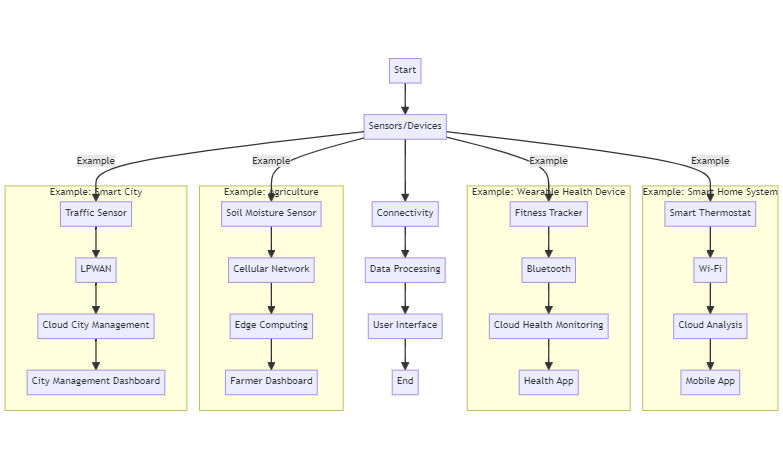
The Internet of Things (IoT) works by connecting various devices to the internet, enabling them to collect, exchange, and act on data. IoT systems typically consist of sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces.
How IoT Works:
- Sensors/Devices: Collect data from their environment (e.g., temperature, motion, light).
- Connectivity: Data is transmitted to a cloud or local server through the internet via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, or other communication protocols.
- Data Processing: The collected data is processed, often using cloud computing, to analyze and derive actionable insights.
- User Interface: Processed data is delivered to end-users via applications, dashboards, or alerts, enabling them to make informed decisions.

Flow Chart:
Real-Life IoT Examples:
- Smart Home Systems: Devices like thermostats, lights, and security cameras are connected to the internet, allowing users to control and monitor their homes remotely through smartphone apps.
- Wearable Health Devices: Fitness trackers and smartwatches collect health-related data (e.g., heart rate, steps) and sync it to apps for real-time health monitoring and fitness insights.
- Agriculture: IoT-enabled sensors monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, providing farmers with data to optimize irrigation and increase yield.
- Smart Cities: IoT devices manage and monitor urban infrastructure, such as traffic lights, waste management systems, and environmental sensors, improving efficiency and sustainability.
By leveraging IoT technology, various industries can enhance operational efficiency, improve decision-making, and offer innovative services to users.
See less
Benefits of Using Drones and IoT Devices in Modern Agriculture: 1. Precision Farming: Drones and IoT devices enable precise monitoring of crops, helping farmers apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides exactly where needed, reducing waste and costs. 2. Real-Time Monitoring: They provide real-time daRead more
Benefits of Using Drones and IoT Devices in Modern Agriculture:
1. Precision Farming: Drones and IoT devices enable precise monitoring of crops, helping farmers apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides exactly where needed, reducing waste and costs.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: They provide real-time data on crop health, soil conditions, and weather, allowing for timely interventions and better decision-making.
3. Increased Efficiency: Automating tasks like planting, monitoring, and spraying increases efficiency and saves labor.
4. Higher Yields: By optimizing resource use and monitoring crop health, these technologies can boost crop yields and quality.
5. Reduced Environmental Impact: Precision application reduces chemical runoff and conserves water, benefiting the environment.
Challenges of Using Drones and IoT Devices in Modern Agriculture:
1. High Costs: Initial investment and maintenance costs for drones and IoT devices can be high, making them less accessible for small farmers.
2. Technical Skills: Farmers need technical knowledge and training to operate and maintain these technologies effectively.
3. Data Management: Handling and analyzing the large amounts of data generated can be overwhelming without proper systems in place.
4. Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet connectivity is essential for IoT devices to function properly, which can be a challenge in remote or rural areas.
5. Regulatory Hurdles: Drones are subject to strict regulations, which can limit their use and require compliance with legal requirements.
See less