What is cloud computing and different areas of cloud computing?
Virtualization is a technology that creates virtual instances of physical hardware resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networks. It allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own operating system and applications. This is achieved through aRead more
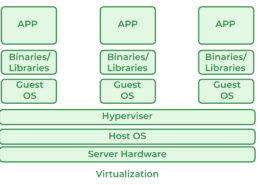
Virtualization is a technology that creates virtual instances of physical hardware resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networks. It allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, each with its own operating system and applications. This is achieved through a software layer called a hypervisor, which manages and allocates resources to each VM.
- Key Concepts:
- Hypervisor: Software that enables multiple VMs to run on a single physical machine. Types include Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted).
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Independent instances that run their own operating systems and applications, sharing the underlying physical hardware.
- Benefits in Cloud Computing:
Top 3 Benefits:
- Resource Efficiency: Virtualization maximizes the use of physical hardware by allowing multiple VMs to run on a single server, reducing the need for additional hardware.
- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware requirements lead to lower capital and operational expenses, including energy consumption and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Virtualization allows for easy scaling of resources. New VMs can be quickly created to handle increased demand, and redundant VMs can be removed when demand decreases.
Other Benefits:
Isolation and Security, Enhanced Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity and Flexibility etc.
Virtualization is a cornerstone of cloud computing, enabling efficient, flexible, and cost-effective resource management.
See less
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet ("the cloud"). This model offers on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources, which can be rapidly provisioned and releaRead more
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). This model offers on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources, which can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Key areas of cloud computing include:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing for scalability and flexibility without investing in physical hardware.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS provides tools and frameworks for building, testing, and deploying applications, speeding up development cycles.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access applications through a web browser without needing to install or maintain software locally. Examples include email services, office productivity suites, and customer relationship management (CRM) software.
4. Serverless Computing:Also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), serverless computing abstracts the underlying infrastructure management from developers. It allows them to focus solely on writing code in the form of functions that are triggered by events, automatically scaling based on demand.
Cloud computing has revolutionized IT by enabling organizations to reduce costs, increase agility, and scale operations more efficiently. It supports a wide range of industries, from startups to large enterprises, offering solutions for storage, data analytics, machine learning, and more, driving innovation and digital transformation across the globe.
See less