Containerization and virtualization differ significantly in resource efficiency and scalability. Resource Efficiency: Containers are more resource-efficient because they share the host operating system’s kernel and system libraries, leading to minimal overhead. This sharing allows containersRead more
Containerization and virtualization differ significantly in resource efficiency and scalability.
Resource Efficiency:
Containers are more resource-efficient because they share the host operating system’s kernel and system libraries, leading to minimal overhead. This sharing allows containers to be lightweight, using fewer CPU, memory, and storage resources compared to virtual machines (VMs). Containers can start almost instantly and utilize system resources more effectively.
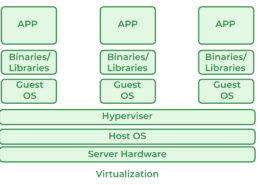
In contrast, virtualization involves running full operating systems within VMs, each with its own kernel. This results in higher overhead as each VM requires a complete OS instance, consuming more CPU, memory, and storage. This overhead can limit the number of VMs you can run on a single host.
Scalability:
Containers excel in scalability due to their lightweight nature. They allow for easy scaling and deployment across multiple hosts with the help of orchestration tools like Kubernetes, which manage containerized applications efficiently.
VMs are less scalable because each VM consumes more resources, which can strain system capacity and complicate scaling efforts. Increasing the number of VMs involves more substantial resource allocation and management challenges.
In summary, containers are generally more efficient and scalable compared to VMs.
See less
Cybersecurity is crucial in today's digital world due to several reasons: 1. Protection of Data: With vast amounts of personal, financial, and organizational data stored online, cybersecurity ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure from unauthorized access, theft, or manipRead more
Cybersecurity is crucial in today’s digital world due to several reasons:
See less1. Protection of Data: With vast amounts of personal, financial, and organizational data stored online, cybersecurity ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure from unauthorized access, theft, or manipulation.
2. Prevention of Cyber Attacks: As cyber threats evolve and become more sophisticated, cybersecurity measures help in detecting, preventing, and mitigating various types of cyber attacks such as malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. attacks can disrupt operations, steal data, and cause financial losses.
3. Protection of Infrastructure: Critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, transportation, and healthcare depend on interconnected systems and networks. Cybersecurity helps in securing these infrastructures from cyber threats that could potentially impact public safety and national security.
4. Privacy and Trust: Maintaining cybersecurity fosters trust among users and customers. It assures individuals that their personal information is handled responsibly and securely, enhancing confidence in digital transactions and online services.
5. Legal Requirements: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements and standards related to data protection and cybersecurity. Adhering to these regulations not only helps in avoiding legal repercussions but also demonstrates commitment to protecting stakeholders’ information.
In essence, cybersecurity is vital for safeguarding digital assets, ensuring business resilience, maintaining trust, and upholding privacy in an increasingly interconnected and digitalized world.