What emerging technologies do you believe will have the biggest impact on solving global environmental challenges?
- Recent Questions
- Most Answered
- Answers
- No Answers
- Most Visited
- Most Voted
- Random
- Bump Question
- New Questions
- Sticky Questions
- Polls
- Followed Questions
- Favorite Questions
- Recent Questions With Time
- Most Answered With Time
- Answers With Time
- No Answers With Time
- Most Visited With Time
- Most Voted With Time
- Random With Time
- Bump Question With Time
- New Questions With Time
- Sticky Questions With Time
- Polls With Time
- Followed Questions With Time
- Favorite Questions With Time
Mains Answer Writing Latest Questions
-
This answer was edited.
What significant challenges does climate change pose for India, considering its geographical diversity, population size, and economic structure?
-
Challenges: Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of events like cyclones, floods, and droughts can disrupt lives, damage infrastructure, and affect agriculture. Agricultural Impact: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns threaten crop yields, affecting food secRead more
Challenges:
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of events like cyclones, floods, and droughts can disrupt lives, damage infrastructure, and affect agriculture.
- Agricultural Impact: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns threaten crop yields, affecting food security and the livelihoods of millions of farmers.
- Water Scarcity: Melting glaciers and altered rainfall patterns can lead to water shortages, impacting drinking water supply, agriculture, and hydropower generation.
- Health Risks: Rising temperatures and pollution levels can exacerbate health issues, including heat strokes, respiratory problems, and the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- Economic Losses: Climate-related disasters can result in significant economic losses, straining public finances and hampering development efforts.
- Biodiversity Loss: Climate change can lead to habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity, threatening wildlife and ecosystems that are crucial for environmental balance.
Opportunities:
- Renewable Energy Development: India has vast potential for solar, wind, and hydropower. Investing in renewable energy can reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and create jobs.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing climate-smart agricultural practices can improve resilience, increase productivity, and ensure food security.
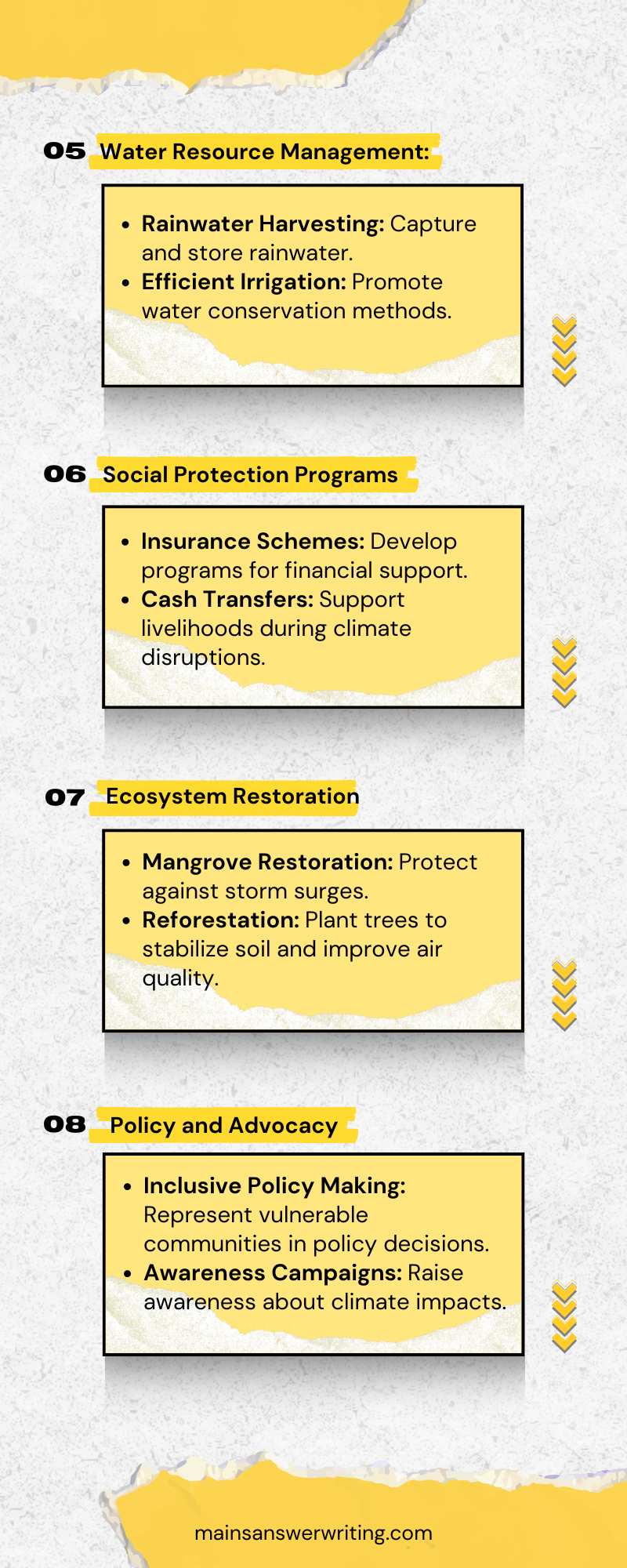
- Water Management: Developing efficient water management systems, such as rainwater harvesting, improved irrigation, and wastewater recycling, can address water scarcity issues.
- Green Infrastructure: Investing in green infrastructure like urban forests, green roofs, and sustainable transport can enhance climate resilience and improve urban living conditions.
- Disaster Preparedness: Strengthening early warning systems and disaster response mechanisms can reduce the impact of extreme weather events and save lives and property.
- Innovation and Technology: Promoting research and development in climate-resilient technologies can drive innovation and support sustainable growth.
- International Collaboration: Engaging in global climate initiatives and partnerships can bring in financial and technical support, enhancing India’s capacity to tackle climate change.
India faces significant challenges due to climate change, but with strategic planning and investment in sustainable practices and technologies, the country can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and development.
See less
-
Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy while balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability involves several strategies: Policy and Regulation: Governments can implement policies that incentivize renewable energy adoption, such as tax credits, subsidies, and carbon pricing.Read more
Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy while balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability involves several strategies:
- Policy and Regulation: Governments can implement policies that incentivize renewable energy adoption, such as tax credits, subsidies, and carbon pricing. These policies can make renewable energy more economically viable and attractive for investment.
- Investment in Technology: Funding research and development in renewable energy technologies can lead to cost reductions and efficiency improvements. Public and private investments can accelerate advancements in solar, wind, hydro, and battery storage technologies.
- Infrastructure Development: Building and upgrading infrastructure to support renewable energy, including smart grids, transmission lines, and storage facilities, ensures reliable and efficient energy distribution.
- Education and Workforce Training: Developing educational programs and training for jobs in the renewable energy sector can create a skilled workforce ready to support the transition, ensuring economic growth through job creation.
- Diversifying the Energy Mix: Gradually increasing the share of renewables in the energy mix while maintaining some conventional energy sources can ensure stability and reliability during the transition period.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in planning and decision-making processes ensures that the transition is inclusive and considers social impacts, thereby fostering public support.
By integrating these strategies, societies can move towards a sustainable energy future that supports economic growth and environmental health.
See less
-
Climate change has affected the global diversity of our planet to extreme extents. The potential long-term impacts of climate change on global biodiversity are given below. Global warming - Global warming is one of the most responsible effect of climate change. Global warming refers to rise in the gRead more
Climate change has affected the global diversity of our planet to extreme extents. The potential long-term impacts of climate change on global biodiversity are given below.
- Global warming – Global warming is one of the most responsible effect of climate change. Global warming refers to rise in the global temperatures which leads to loss of habitat on land and sea and hence affecting the biodiversity of our planet.
- Frequent changes in the weather patterns – Animals often depend on the kind of weather patterns for taking important decisions like the migrating season, reproduction season etc. Due to climate change affecting the weather patterns it causes biological events to fall out of sync and in the long run can disrupt the functioning of the entire ecosystems.
- Decline in wildlife and extinction of species – Climate change affects the natural habitat of many animals thereby causing extinction of those species in the longer run.
Conservation of our biodiversity can be done by the following methods.
- Reducing greenhouse gases by using energy more efficiently and using more renewable sources.
- Restoring damaged ecosystems, protecting more wild spaces, and promoting environmental justice.
- Creating more wildlife corridors and protected green spaces.
- Funding research and monitoring of wildlife.
-
Historical climate events have significantly influenced human societies in various ways, and understanding these impacts can guide our current responses to climate change. Here are some key points: 1. Migration and Displacement Examples: The collapse of the Mayan civilization and the migration of ViRead more
See lessHistorical climate events have significantly influenced human societies in various ways, and understanding these impacts can guide our current responses to climate change. Here are some key points:
1. Migration and Displacement
- Examples: The collapse of the Mayan civilization and the migration of Viking populations were partly due to prolonged droughts and climate shifts.
- Implication: Current climate change may lead to increased migration and displacement, highlighting the need for policies that support affected populations.
2. Agricultural Practices
- Examples: The Little Ice Age affected crop yields in Europe, leading to food shortages and social unrest.
- Implication: Studying past agricultural adaptations can help modern societies develop resilient farming practices and food security strategies.
3. Economic Structures
- Examples: Societies reliant on specific climates, such as the ancient Egyptians with the Nile, faced economic challenges during climate fluctuations.
- Implication: Diversifying economies and reducing reliance on climate-sensitive resources can enhance resilience.
4. Social Conflicts
- Examples: Resource scarcity, driven by climate events, has historically led to conflicts, such as the Syrian civil war partly influenced by a severe drought.
- Implication: Understanding these links can inform conflict prevention strategies and promote cooperation over shared resources.
5. Technological Innovation
- Examples: Societies often innovate in response to climate challenges, such as the development of irrigation systems in arid regions.
- Implication: Encouraging research and development of sustainable technologies can help mitigate the effects of climate change.
6. Policy and Governance
- Examples: Responses to historical climate crises often shaped governance structures, as seen in the establishment of early disaster response frameworks.
- Implication: Current policy-making can benefit from adaptive governance approaches that emphasize flexibility and responsiveness to climate impacts.
Conclusion
By studying historical climate events and their effects on societies, we can better prepare for and respond to contemporary climate challenges. This knowledge underscores the importance of resilience, adaptability, and cooperation in tackling the ongoing climate crisis.
Do upwelling of magma due in subduction in east of Ring of fire affects the Phenomenon of El-Nino and La-Nina because of Geothermal heat and hotspots around Circum-Pacific belt.
-
The relationship between the Ring of Fire, subduction zones, and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is complex and still not fully understood. While there are some theoretical connections, the evidence is still being researched and debated. Here's a summary of the potential connections: SubductRead more
The relationship between the Ring of Fire, subduction zones, and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is complex and still not fully understood. While there are some theoretical connections, the evidence is still being researched and debated. Here’s a summary of the potential connections:
- Subduction zones and magma upwelling: Subduction zones, like those found along the Ring of Fire, can lead to the upwelling of magma from the Earth’s mantle. This process can release large amounts of heat and volatiles into the overlying crust, potentially influencing the surrounding oceanic and atmospheric circulation patterns.
- Geothermal heat and hotspots: The Circum-Pacific belt is indeed characterized by numerous hotspots, such as those around Indonesia, Philippines, and Mexico, which are associated with mantle plumes and upwelling of magma. These hotspots can release significant amounts of heat into the oceanic crust, which can in turn affect global climate patterns.
- ENSO and Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO): ENSO is a complex climate phenomenon characterized by fluctuations in sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The PDO is a related climate pattern that affects the Pacific Northwest coast of North America and is characterized by warmer or cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures.
- Linkages between subduction zones, ENSO, and PDO: Some researchers have suggested that changes in the magma upwelling rates at subduction zones could influence the development of ENSO events. For example:
- Faster magma upwelling might lead to increased volcanic activity, which could inject more aerosols into the stratosphere, cooling the planet and favoring La Niña conditions.
- Slower magma upwelling might result in reduced volcanic activity, allowing for more heat to escape from the Earth’s interior and favoring El Niño conditions.
- Other factors influencing ENSO: Many other factors contribute to ENSO variability, including:
- Atmospheric circulation patterns (e.g., trade winds)
- Oceanic currents (e.g., California Current)
- Volcanic eruptions (not just those related to subduction zones)
- Changes in global atmospheric circulation patterns (e.g., North Atlantic Oscillation)
While there is some theoretical basis for connecting subduction zones, geothermal heat, and hotspots to ENSO variability, the evidence is still limited and inconclusive. More research is needed to understand the complex relationships between these factors.
See less
-
Air pollution is the contamination of atmospheric air by chemical, physical, or natural agents, making it unsuitable and harmful for breathing. Primary pollutants like carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur oxides, aerosols, and fine particulates have serious effects on both the environment and human health.Read more
Air pollution is the contamination of atmospheric air by chemical, physical, or natural agents, making it unsuitable and harmful for breathing. Primary pollutants like carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur oxides, aerosols, and fine particulates have serious effects on both the environment and human health.
Observed Climate Changes:
- Global Warming by gases like CFCs and Methane.
- High global temperature causing rise in sea levels and coastal flooding by rapid melting of polar ice caps.
- Severe droughts and torrential rains.
Impact on Human Health:
Exposure to –
- UV radiation (due to the depletion of the ozone layer) weakens the immune system, causes sunburn and even cancer.
- Air pollutants can cause chronic diseases like lung cancer and asthma.
- Air containing even 0.001% of carbon monoxide can cause drowsiness, collapse, coma, or even death.
- Volatile Compounds like Benzene can cause mutations in foetus and other reproductive problems.
Impact on Environment:
Gaseous air pollutants can cause damage to –
- Leaves of crop plants and flower buds (by acid rain).
- Nutrient content and growth potential of plants.
- Phytoplankton and zooplankton (by UV radiation).
The Indian Government, observing the alarming effects of air pollution, has implemented certain measures such as the Air Prevention and Control of Pollution Act and Central Motor Act to mitigate the effects of air pollution. However, more such preventive measures are needed to address the emerging concerns.
See less


"Emerging Technologies and Global Environmental Solutions" encapsulates the innovative approaches and advancements aimed at addressing pressing environmental challenges worldwide. Technologies like renewable energy sources (solar, wind, and hydroelectric power) and sustainable agriculture practicesRead more
“Emerging Technologies and Global Environmental Solutions” encapsulates the innovative approaches and advancements aimed at addressing pressing environmental challenges worldwide. Technologies like renewable energy sources (solar, wind, and hydroelectric power) and sustainable agriculture practices play pivotal roles. These innovations offer cleaner alternatives to traditional energy sources and mitigate environmental degradation caused by intensive farming methods.
Additionally, advancements in waste management technologies, such as recycling and waste-to-energy processes, contribute significantly to reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Smart city initiatives leverage technology to optimize resource use, enhance urban sustainability, and reduce carbon footprints through efficient transportation systems and infrastructure.
Biotechnological innovations, like genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and biofuels, hold promise for enhancing agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impacts. Moreover, emerging technologies in water purification and conservation are crucial for addressing global water scarcity challenges.
Collectively, these technologies underscore a growing trend towards sustainable development, where technological innovation intersects with environmental stewardship to foster a cleaner, greener future for generations to come. Embracing and scaling these solutions globally is essential for achieving environmental sustainability and mitigating the impacts of climate change on a planetary scale.
See less