How can machine learning and artificial intelligence be leveraged to enhance threat detection and response in cybersecurity, and what are the potential challenges associated with their implementation?
In the future, technology will revolutionize healthcare with AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine, improving disease detection and treatment while cutting costs. Autonomous vehicles will enhance transportation safety and efficiency, reducing accidents and dependence on fossil fuels. VR anRead more
In the future, technology will revolutionize healthcare with AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine, improving disease detection and treatment while cutting costs. Autonomous vehicles will enhance transportation safety and efficiency, reducing accidents and dependence on fossil fuels. VR and AR will transform communication and learning, bridging distances and reshaping education and remote work. IoT will create smart homes that automate tasks and optimize energy use, simplifying daily life. Advancements in renewable energy will combat climate change by fostering greener, more resilient energy systems. Overall, technology promises to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and connectivity across various domains, offering solutions to everyday challenges in unprecedented ways.
See less

Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) offer significant potential to enhance threat detection and response in cybersecurity. Here's an overview of how they can be leveraged and the associated challenges: Leveraging ML and AI in Cybersecurity: 1. Anomaly detection: - ML algorithms caRead more
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) offer significant potential to enhance threat detection and response in cybersecurity. Here’s an overview of how they can be leveraged and the associated challenges:
Leveraging ML and AI in Cybersecurity: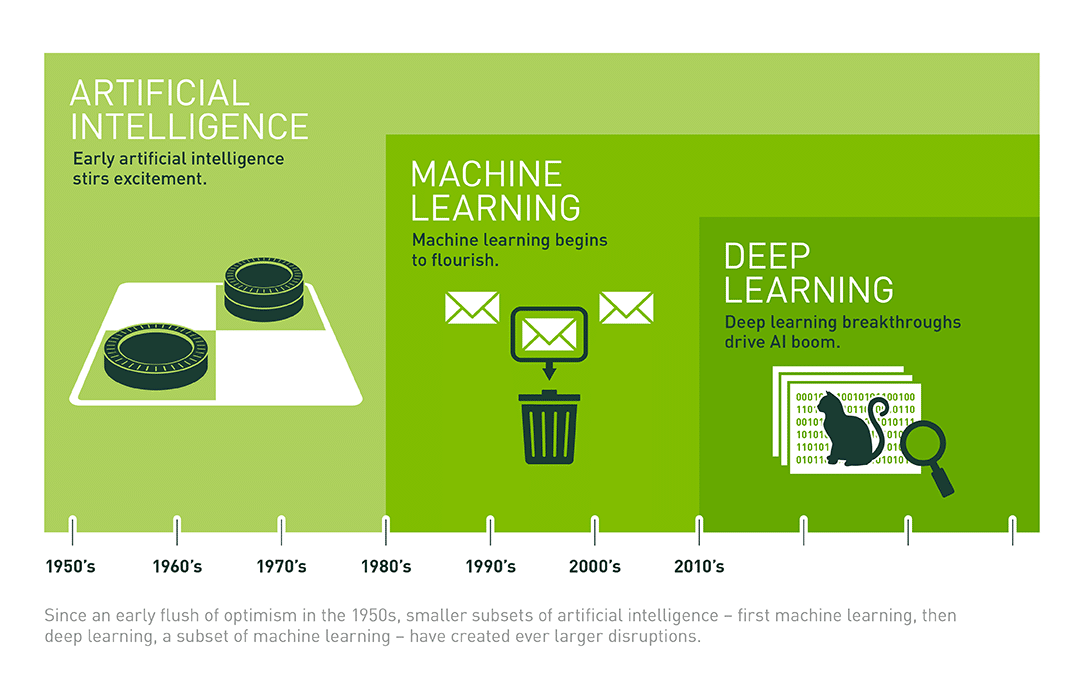
1. Anomaly detection:
– ML algorithms can analyze network traffic patterns to identify unusual behaviors that may indicate a threat.
– AI can establish baselines of normal activity and flag deviations in real-time.
2. Threat intelligence:
– ML can process vast amounts of threat data from multiple sources to identify emerging threats and attack patterns.
– AI can correlate information to provide context and prioritize threats.
3. Automated response:
– AI-powered systems can initiate automated responses to contain threats quickly.
– This can include isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IPs, or initiating backups.
4. Behavioral analysis:
– ML can model user and entity behavior to detect insider threats or compromised accounts.
5. Malware detection:
– AI can analyze code structure and behavior to identify new or evolving malware strains.
6. Predictive analytics:
– ML models can predict potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors based on historical data and current trends.
7. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
– NLP can analyze security logs and reports to extract relevant information and insights.
Challenges in Implementation:
1. Data quality and quantity:
– ML/AI models require large amounts of high-quality, diverse data for training.
– Obtaining comprehensive, up-to-date cybersecurity data can be challenging.
2. False positives:
– Overly sensitive AI systems may generate excessive false alarms, leading to alert fatigue.
3. Adversarial AI:
– Attackers can use AI to create more sophisticated threats or to evade AI-based defenses.
4. Explainability:
– The “black box” nature of some AI algorithms can make it difficult to explain or justify security decisions.
5. Skill gap:
– There’s a shortage of professionals with expertise in both cybersecurity and AI/ML.
6. Ethical concerns:
– AI-powered monitoring raises privacy concerns, especially in contexts like employee behavior analysis.
7. Keeping pace with evolving threats:
– AI models need constant updating to remain effective against rapidly evolving cyber threats.
8. Integration with existing systems:
– Implementing AI/ML solutions alongside legacy security infrastructure can be complex.
9. Regulatory compliance:
– Ensuring AI-driven security measures comply with data protection regulations can be challenging.
10. Resource requirements:
– Implementing and maintaining AI/ML systems can be computationally intensive and expensive.
While ML and AI offer powerful tools for enhancing cybersecurity, their effective implementation requires careful planning, ongoing maintenance, and a balance between automation and human oversight. Organizations must weigh the benefits against the challenges and develop strategies to address these issues as they integrate AI/ML into their cybersecurity frameworks.
See less