What are the Ethical Concerns of Genome Editing?
Principle of Gel Electrophoresis: Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge. The principle behind this method is that molecules move through a gel when an electric current is applied. The gel, usually made of agarose or polyacrylamide, aRead more
Principle of Gel Electrophoresis: Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge. The principle behind this method is that molecules move through a gel when an electric current is applied. The gel, usually made of agarose or polyacrylamide, acts like a sieve. Smaller molecules move faster and travel farther through the gel, while larger molecules move more slowly. The gel is placed in a buffer solution that helps conduct the electric current. When the current is applied, negatively charged molecules, like DNA, move towards the positive electrode.
Uses of Gel Electrophoresis:
- DNA Analysis: Gel electrophoresis is widely used in genetics to analyze DNA fragments. It helps in DNA fingerprinting, which is used in forensic science to identify individuals.
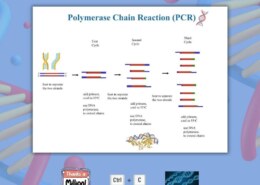
- PCR Product Verification: After performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR), scientists use gel electrophoresis to check if the correct DNA fragment has been amplified.
- RNA Analysis: It is used to study RNA molecules, which can help in understanding gene expression and regulation.
- Protein Separation: Researchers use this technique to separate and study proteins, which can be important in diagnosing diseases and understanding biological processes.
- Cloning and Gene Mapping: It helps in cloning by verifying the size of inserted DNA fragments and in mapping genes to understand their structure and function.
In summary, gel electrophoresis is a versatile tool that helps scientists separate and analyze molecules, providing crucial insights in various fields of biology and medicine.
See less
Genome Editing is a process by which alterations are made to the DNA (genetic material) of an organism. These genetic alterations can cause changes in physical traits like hair colour, eye colour, body height, etc. Editing can be done on somatic cells as well as germline cells. This process has manyRead more
Genome Editing is a process by which alterations are made to the DNA (genetic material) of an organism. These genetic alterations can cause changes in physical traits like hair colour, eye colour, body height, etc. Editing can be done on somatic cells as well as germline cells. This process has many prospects for example, it can be used to prevent, treat or cure certain diseases.
Inspite of the benefits this technology offers, there are various ethical issues involved.
Some concerns are:
1) Some arguments say that when germline genome is edited, there is alteration in the genome of embryo at its earliest stages, which may effect every cell. This means that it has an impact not only on the person who may result, but also on his/her descendants.
2) Should people be allowed to use this technology to embrace basic human characteristics like height or skin colour?
3) It is difficult to ensure that people completely understand the risks and benefits involved with altering their genome.
4) The high cost of genome editing may make it available only to the wealthy section of society, thus ensuring fair and equitable access is a big challenge.
5) Genetically engineered humans may feel alienated from themselves or feel a confused identity.
See less