what do you mean by capitalism and what do u mean by socialism? Which countries follow socialism and why?
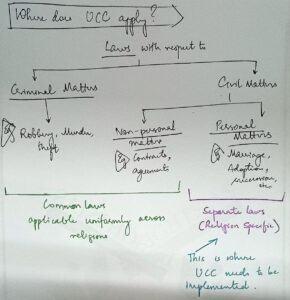
Divorce laws worldwide vary significantly based on cultural, religious, and legal frameworks. Evaluating divorce laws involves assessing their effectiveness, fairness, and impact on individuals and society. Here are key aspects to consider: Legal Grounds for Divorce: No-Fault vs. Fault-Based: Laws mRead more
Divorce laws worldwide vary significantly based on cultural, religious, and legal frameworks. Evaluating divorce laws involves assessing their effectiveness, fairness, and impact on individuals and society. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Legal Grounds for Divorce:
- No-Fault vs. Fault-Based: Laws may allow divorce on grounds such as irreconcilable differences (no-fault) or specific reasons like adultery or cruelty (fault-based).
- Divorce Process:
- Simplicity vs. Complexity: The ease and complexity of the divorce process vary. Some jurisdictions require lengthy legal procedures and waiting periods, while others offer simplified processes.
- Division of Assets and Liabilities:
- Equitable Distribution: Laws dictate how marital property, debts, and assets acquired during the marriage are divided upon divorce. Some jurisdictions follow equitable distribution principles, ensuring a fair split based on various factors.
- Child Custody and Support:
- Best Interest of the Child: Laws prioritize the welfare of children, determining custody arrangements and support payments based on factors like parental capability and children’s needs.
- Spousal Support (Alimony):
- Entitlement and Calculation: Laws address whether and how much financial support a spouse may receive post-divorce, considering factors like duration of marriage, earning capacity, and financial contributions.
- Impact on Individuals and Families:
- Emotional and Financial Stability: Divorce laws can impact individuals’ emotional well-being and financial stability. Supportive legal frameworks may facilitate smoother transitions and fair outcomes.
- Social and Cultural Considerations:
- Adaptation to Changing Norms: Divorce laws evolve to reflect societal norms and values, such as recognition of same-sex marriages and diverse family structures.
- Legal Reform and Accessibility:
- Ease of Access: Evaluating how accessible divorce procedures are to individuals, including affordability, availability of legal aid, and cultural acceptance.
- International Comparison:
- Variations Across Jurisdictions: Comparative analysis helps understand how different legal systems handle divorce, highlighting best practices and areas for improvement.
- Long-Term Effects:
- Impact on Children and Society: Research assesses the long-term effects of divorce laws on children’s well-being, family stability, and societal cohesion.
In conclusion, evaluating divorce laws involves examining their legal foundations, procedural fairness, social implications, and effectiveness in promoting individual rights and societal welfare. Continuous evaluation and adaptation of these laws are crucial to meet evolving societal needs and ensure justice for all parties involved in divorce proceedings.

Capitalism and socialism are contrasting economic systems with different approaches to ownership, production, and distribution of goods and services. Capitalism is characterized by private ownership of property and means of production. In this system, individuals and businesses operate in a free marRead more
Capitalism and socialism are contrasting economic systems with different approaches to ownership, production, and distribution of goods and services.
Capitalism is characterized by private ownership of property and means of production. In this system, individuals and businesses operate in a free market, driven by supply and demand. Key features include:
1.Profit motivation
2.Competition between businesses
3.Limited government intervention
4.Individual economic freedom
Socialism, conversely, advocates for collective or state ownership of resources and means of production. Its main characteristics include:
1.Public ownership of key industries.
2.Central economic planning.
3.Emphasis on equality and wealth redistribution.
4.Greater government involvement in the economy.
Proponents of capitalism argue it fosters innovation, efficiency, and economic growth.
Supporters of socialism believe it promotes fairness and meets everyone’s basic needs. Detractors argue it stifles innovation and individual liberty.
In practice, most modern economies are mixed systems, incorporating elements of both capitalism and socialism. The balance between these elements varies widely among different countries, reflecting their unique historical, cultural, and political contexts.
examples of countries with strong capitalist elements United States, Singapore, Hong Kong, Switzerland. Whereas Countries with stronger socialist elements include Cuba,Vietnam, China, North Korea.
See less