AI integrates into robotics by using advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques. It enhances perception through computer vision and sensor fusion, enabling robots to interpret visual and sensory data accurately. Decision-making improves with machine learning, allowing robots to learn from eRead more
AI integrates into robotics by using advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques. It enhances perception through computer vision and sensor fusion, enabling robots to interpret visual and sensory data accurately. Decision-making improves with machine learning, allowing robots to learn from experience and optimize actions via reinforcement learning. AI advances motion control by aiding in path planning and precise manipulation of objects. Additionally, natural language processing allows robots to understand and interact with human language, improving human-robot communication.
Benefits:
Efficiency: AI-driven robots perform complex tasks faster and with greater accuracy.
Autonomy: AI enables robots to operate independently in dynamic environments.
Adaptability: Robots learn and adapt to new tasks and conditions without explicit reprogramming.
Challenges:
Complexity: Developing and integrating sophisticated AI algorithms is technically demanding and resource-intensive.
Ethics and Security: Ensuring AI systems are ethical, safe, and secure from misuse is critical.
Reliability: AI models require extensive training data and validation to ensure consistent performance.
See less
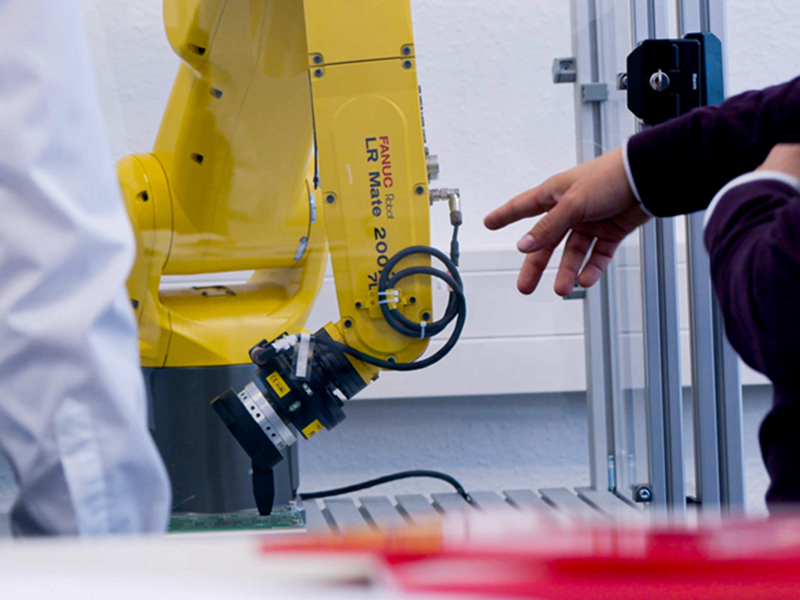




A robotic system consists of several main components that work together to perform various tasks. The main components include sensors, actuators, controllers, and effectors. Sensors provide information about the system's environment, such as temperature, pressure, proximity, or vision. These inputsRead more
A robotic system consists of several main components that work together to perform various tasks. The main components include sensors, actuators, controllers, and effectors.
Sensors provide information about the system’s environment, such as temperature, pressure, proximity, or vision. These inputs are then sent to the controller, which processes the data and makes decisions based on it. The controller directs the actuators to perform the desired actions. Actuators are the physical components that move and manipulate the robot, such as motors, pistons, or hydraulic systems. Effectors are the tools or devices that directly interact with the environment, such as grippers, wheels, or arms.
These components work together in a robotic system by constantly communicating and exchanging information. The sensors detect changes in the environment and send this data to the controller, which interprets the information and sends commands to the actuators to move the robot accordingly. The effectors then interact with the environment to perform tasks, such as picking up objects or navigating through a space. Overall, the components of a robotic system work in collaboration to enable the robot to complete its designated tasks efficiently and effectively.
See less