Since India's independence, Indian scientists and technologists have significantly contributed to the nation's development across various fields: Key Achievements Space Technology: Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, the father of the Indian space program, founded ISRO, which launched satellites like Aryabhata andRead more
Mains Answer Writing Latest Questions
How linguistic and regional diversity of India to growth of country and what make it differ from another countries?
-
India's linguistic and regional diversity profoundly influences its growth and development in unique ways compared to other countries. With over 1,600 languages and various distinct cultures, India's diversity fosters a rich tapestry of traditions, knowledge systems, and societal practices. This divRead more
India’s linguistic and regional diversity profoundly influences its growth and development in unique ways compared to other countries. With over 1,600 languages and various distinct cultures, India’s diversity fosters a rich tapestry of traditions, knowledge systems, and societal practices. This diversity acts as a catalyst for creativity, innovation, and resilience in the face of challenges.
Economically, linguistic diversity enhances India’s ability to engage in global trade and diplomacy, leveraging multilingual talent for international relations and business negotiations. Culturally, it enriches artistic expressions, literature, and traditions, attracting global interest and tourism.
Unlike many countries with dominant national languages, India’s federal structure and recognition of multiple official languages empower states and regions to preserve and promote their linguistic heritage. This decentralization facilitates local governance and development tailored to regional needs, fostering inclusive growth across diverse communities.
However, managing such diversity requires robust policies for language education, cultural preservation, and equitable access to opportunities. India’s commitment to pluralism and unity in diversity serves as a model for harmonizing varied identities within a democratic framework, contributing to its distinct socio-economic trajectory amidst global homogenization trends.
See less
-
Technology act like a catalyst in process of education.It made education accessible to remote areas, breaking geographical barriers. Online courses, webinars, and digital libraries have democratized learning, allowing anyone with internet access to acquire new skills and knowledge. It has personalizRead more
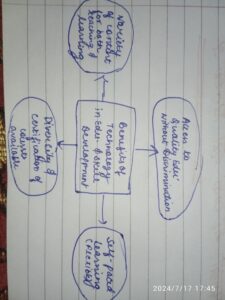
Technology act like a catalyst in process of education.It made education accessible to remote areas, breaking geographical barriers. Online courses, webinars, and digital libraries have democratized learning, allowing anyone with internet access to acquire new skills and knowledge.
It has personalized learning experiences, adapting to individual learning styles and paces. Virtual reality technologies have made learning more interactive and engaging.
Technology has also transformed skill development.Open and distance learning also played a supporting role with technology . This made Online certification courses, coding bootcamps, and MOOCs have made it easier for individuals to acquire industry-relevant skills. Digital portfolios, quizzes and online assessments have made skill validation more transparent and efficient.
In nutshell technology has not only made education and skill development more democratized but has also made it more inclusive and personalized.
See less
What is the most significant yet least recognized contribution of India to global environmental sustainability efforts in the last century, and how has it impacted international policy and practice?
-
India's Significant Yet Least Recognized Contribution to Global Environmental Sustainability Forest Conservation and Community-Based Resource Management One of India's most significant yet least recognized contributions to global environmental sustainability is its pioneering work in forest conservaRead more
India’s Significant Yet Least Recognized Contribution to Global Environmental Sustainability
Forest Conservation and Community-Based Resource Management
One of India’s most significant yet least recognized contributions to global environmental sustainability is its pioneering work in forest conservation and community-based resource management. The Joint Forest Management (JFM) program, initiated in the 1980s, epitomizes this effort. JFM encourages local communities to engage in the protection and management of forests, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards sustainable practices. This model has empowered communities, enhanced biodiversity, and improved forest cover, directly influencing carbon sequestration efforts.
Impact on International Policy and Practice
India’s success with JFM has inspired similar initiatives globally. The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) and other international bodies have acknowledged India’s approach, promoting community participation in forest management as a best practice. Moreover, this model has influenced international policies such as the REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) mechanism under the UNFCCC, which incorporates community-based strategies to enhance carbon storage and sustainable development.
Overall, India’s innovative approach to integrating local communities in forest conservation has made a lasting impact on global environmental policies, promoting sustainable practices that are both effective and inclusive.
See less
-
1. Holistic approach: India combines ancient philosophies, practices, and wisdom with cutting-edge scientific and technological advancements, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the world. 2. Interdisciplinary learning: This approach encourages students to bridge the gap between traditioRead more
1. Holistic approach: India combines ancient philosophies, practices, and wisdom with cutting-edge scientific and technological advancements, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of the world.
See less
2. Interdisciplinary learning: This approach encourages students to bridge the gap between traditional and modern disciplines, enabling innovative problem-solving.
3. Respect for indigenous knowledge: By valuing traditional knowledge systems, India promotes cultural preservation and the inclusion of diverse perspectives in STEM fields.
4. Sustainable solutions: The integration of traditional and modern approaches can lead to the development of more sustainable and environmentally-friendly technologies.
5. Enriched curriculum: India’s model can inspire other countries to enhance their STEM curricula with elements of traditional knowledge, creating a richer educational experience for students.
-
Data Privacy: Collecting, storing and using user data responsibly to respect individual rights. Bias and Fairness: Fixing biases in the data that can lead to discriminatory outcomes and perpetuate existing inequalities. Transparency: Making AI explainable so humans can understand and challenge algorRead more
- Data Privacy: Collecting, storing and using user data responsibly to respect individual rights.
- Bias and Fairness: Fixing biases in the data that can lead to discriminatory outcomes and perpetuate existing inequalities.
- Transparency: Making AI explainable so humans can understand and challenge algorithmic decisions.
- Accountability: Establishing clear accountability for AI systems and mechanisms for recourse when harm occurs.
- Informed Consent: Getting explicit consent from users when collecting and processing their data.
- Security: Protecting AI from cyber attacks that could compromise its integrity and lead to harm.
- Autonomy and Control: Balancing automation with human oversight so AI supports human decision making not replaces it.
- Social Impact: Considering the broader societal implications of AI deployment, including job displacement and economic inequality.
- Misuse: Preventing AI from being used for malicious purposes like deepfakes or autonomous weapons.
- Inclusivity: Having diverse representation in AI teams to fix biases and build more equitable systems.
Addressing these ethical considerations is crucial for developing AI algorithms that are fair, transparent, and beneficial to society.
See less
-
The Paleolithic Age, also known as the Old Stone Age, spans a vast period of prehistory from about 2.5 million years ago to around 10,000 years ago. It is characterized by the use of stone tools crafted by early human ancestors such as Homo habilis and Homo erectus. During this era, humans were primRead more
The Paleolithic Age, also known as the Old Stone Age, spans a vast period of prehistory from about 2.5 million years ago to around 10,000 years ago. It is characterized by the use of stone tools crafted by early human ancestors such as Homo habilis and Homo erectus. During this era, humans were primarily hunter-gatherers, relying on hunting wild animals and gathering edible plants for sustenance. Their societies were small and nomadic, moving in search of food and shelter.
Artistic expressions began to emerge in the form of cave paintings, sculptures, and personal adornments, showcasing early humans’ cognitive abilities and symbolic thinking. Fire was mastered during this time, serving both as a source of warmth and protection and for cooking food, which improved nutrition and energy efficiency.
The Paleolithic Age saw gradual advancements in tool technology, from simple choppers and hand axes to more refined implements. Social structures evolved within communities, likely organized around kinship ties and cooperative hunting. This era laid the foundation for human adaptation and innovation, setting the stage for future developments such as agriculture and settled civilizations in the Neolithic Age that followed.
See less
-
Benefits of Migrating Enterprise Applications to the Cloud: Cost Savings Reduced Costs on IT Infrastructure: They do not directly invest in comericial equipment and services such as on-site hardware (servers, storage, networking equipment) and data centers and their cooling systems Pay-as-You-Go ModRead more
Benefits of Migrating Enterprise Applications to the Cloud:
Cost Savings
Reduced Costs on IT Infrastructure: They do not directly invest in comericial equipment and services such as on-site hardware (servers, storage, networking equipment) and data centers and their cooling systems
Pay-as-You-Go Model: Most cloud providers align this cost on the actual usage to enable the up or down scaling on cost outlay.
-Rapid scaling: Optional users may be increased or decreased instantly in response to a range of rarely occurring or unpredictable high levels of demand, for example at the end of calendar years, academic years or fiscal years. Faster time to market: The fast deployment of applications and services ensures that new products/services are developed and launched on the market faster.Higher Innovation
-Access to Cutting-Edge Technologies: Get more access to the cloud services, such as AI/ML, big data and IoT, to transform business models for growth.
-Focus on Core Business: Divert IT infrastructure responsibilities and workload leaving room for IT to deliver more on strategic concerns that supports the business.Improved Security:
-Strong Security: Cloud providers invest a lot of money in security and its deployment and follow the best practices to shield data and applications from threats.Difficulties in Migrating Enterprise Applications to the Cloud:
Security:
Data Breaches: The cloud providers may offer strong protection measures but there are still data leaks.
Compliance Issues: Implementing privacy rules for data storage sharing particularly in the current increased cloud utilize (for example the GDPR or CCPA ).Vendor Lock-in:
Dependence on the Cloud Provider: Data and applications are moved to a specific cloud provider and this make it complex to do the same with another in future hence creating vendor lock in.Integration Challenges:
Integration with Existing Systems: However, they also posed some important challenges that include the following: The integration of the cloud-based applications with the existing on site systems and applications is always a challenge.Cost Management:
Unexpected Costs: The following costs are also possible if not checked frequently; data transfer charges, storage fees, and the emergence of surge in usage among others.Data Migration:
Data Quantity: Heavy volume data migrating into the cloud will be complex and time-consuming potentially causing disruption to daily business routines.Skilling Gap:
See less
-Cloud Savvy: For successful handling and management of applications powered through cloud, organizations must build their skills.

Remote work infographic design
Remote work infographic design
See less