"It is a regret that Article 44 has remained a dead letter" said Justice Y V Chandrachud in Shah Bano judgement (1985). Our constitution-makers have placed 'Uniform Civil Code(Article 44)' under Directive principles of State Policy(Part IV). Need for UCC to balance diversity and ensure social justiRead more
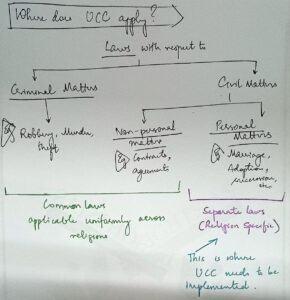
“It is a regret that Article 44 has remained a dead letter” said Justice Y V Chandrachud in Shah Bano judgement (1985). Our constitution-makers have placed ‘Uniform Civil Code(Article 44)’ under Directive principles of State Policy(Part IV).
Need for UCC to balance diversity and ensure social justice
1) It enhances ‘Secularism’ – mentioned in Preamble and a part of Basic structure.
2) It is based on ‘Equality’ – a fundamental right (Article 14)
3) Personal laws are usually against women and marginal, vulnerable sections.
For example, Shariat – allows polygamy (Sarala Mudgal Case)
5) States like Goa, Uttarkhand have adopted UCC after legislative consensus
6) Supreme Court has supported its implementation in multiple instances.
Challenges to implement UCC
1. Article 26 provides for the right to manage one’s own religious matters.
2. Debate of – Fundamental Rights(Article 26) v/s DPSPs(Article 44)
3. STs have customary laws protected by the constitution itself.
4. Apprehensions of imposition of majoritarian values on minority
5. Accommodating diversity
Way forward
1) 22nd Law commission sought public consultation process on UCC
2) Consensus building that UCC is necessary
3) In the short-term personal laws can be codified phase-wise
4) UCC should not be imposed right away through an ordinance, it should pass through parliamentary debates and deliberations
5) Political parties should rise above differences for the common good of all
A fundamental change in people’s mindset is required for UCC’s implementation.
See less
Introduction: India's complex religious landscape and historical background make religion and politics there closely intertwined. The interaction between these two domains has a major impact on the country's political structure. Historical Context: India has a millennium-long tradition of religiousRead more
Introduction:
India’s complex religious landscape and historical background make religion and politics there closely intertwined. The interaction between these two domains has a major impact on the country’s political structure.
Historical Context:
India has a millennium-long tradition of religious plurality, embracing Buddhism, Sikhism, Jainism, Islam, Christianity, and other faiths. Throughout the colonial era, the British government implemented a policy known as “divide and rule,” which deepened religious tensions and planted the seeds of communalism. The Indian Constitution created a secular framework after independence that guaranteed freedom of religion and maintained the state’s impartiality on religious issues.
Secularism and Its Challenges:
Being unique, Indian secularism aims to strike a compromise between state neutrality and religion plurality. Indian secularism recognises the religious identities of its citizens, as contrast with Western secularism, which promotes a rigid separation of church and state. This inclusive strategy seeks to treat all religions with equal respect.
But problems still exist. Political parties frequently use religious feelings to win over voters, which polarises society. Discussions on the nature of Indian secularism and how it should be implemented have been triggered by the advent of majoritarian politics, particularly with the spread of Hindutva ideology.
Communalism and Social Cohesion:
India’s social cohesiveness is seriously threatened by communalism, which has a propensity to erect religious divisions. Interfaith harmony is vulnerable to violent incidents like the anti-Sikh riots in 1984, the Gujarat riots in 2002, and more recent conflicts. These kinds of gatherings frequently have political undertones, with opposing factions using religious identities as a political tool.
Legal and Constitutional Safeguards:
The Indian Constitution offers a number of protections to maintain secularism. While Articles 14 and 15 establish equality before the law and forbid discrimination based on religion, Articles 25–28 guarantee religious freedom. The use of religion in political campaigns is outlawed by the Representation of the People Act of 1951. Nonetheless, there is still uneven application of these regulations.
Conclusion:
In India, the relationship between politics and religion is a complicated and dynamic phenomena. Political exploitation of religious identities persists in undermining the secular framework’s goal of preserving religious diversity and fostering peace. Sustaining India’s pluralistic democracy requires bolstering secular ideals, encouraging interreligious dialogue, and guaranteeing impartial law enforcement.
See less