Examine the steps taken by the government to advance the internationalization of the Indian rupee, such as the attempts to increase its usage in investment and trade transactions, and determine whether or not they have the potential to lessen India’s ...
Implications of Growing Emphasis on Sustainable and Climate-Friendly Development on India's External Sector Introduction The global shift towards sustainable and climate-friendly development is reshaping various facets of India's external sector. This emphasis impacts India's export diversification,Read more
Implications of Growing Emphasis on Sustainable and Climate-Friendly Development on India’s External Sector
Introduction
The global shift towards sustainable and climate-friendly development is reshaping various facets of India’s external sector. This emphasis impacts India’s export diversification, foreign investment flows, and international trade agreements. This analysis explores these implications and evaluates the government’s policies to navigate these emerging challenges.
Implications on Export Diversification
Shift in Export Demand: As countries commit to climate goals, there is an increasing demand for sustainable and green products. India’s export sector must adapt to these changing preferences by diversifying into eco-friendly goods and services. For example, India’s exports of organic and certified sustainable products have seen growth as global consumers prioritize sustainability.
Increased Competitiveness: Emphasizing sustainability can enhance India’s competitiveness in global markets. The Gujarat-based solar panel manufacturer, Waaree Energies, has successfully tapped into international markets by producing green energy solutions, aligning with global demand for renewable energy products.
Challenges: Transitioning to sustainable practices poses challenges such as higher production costs, certification requirements, and investment in green technologies. Indian firms, especially in sectors like textiles and chemicals, face difficulties in meeting international sustainability standards, which could affect their export performance.
Implications on Foreign Investment Flows
Increased Foreign Investment in Green Projects: There is a growing interest in investing in India’s green infrastructure and sustainable development projects. Initiatives like the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) are attracting foreign investments into renewable energy and green infrastructure. For example, Global Infrastructure Partners has invested in India’s green energy sector, reflecting a shift towards sustainability-focused investments.
Regulatory Challenges: Foreign investors are increasingly focusing on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria when making investment decisions. Indian policies need to align with these criteria to attract investment. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced regulations requiring listed companies to disclose their ESG performance, which could affect foreign investment flows.
Investment in Technology and Innovation: To attract foreign investment, India needs to enhance its technology infrastructure and innovation capacity in green technologies. The Startup India Initiative supports innovation in sustainable technologies, positioning India as a hub for green tech investments.
Implications on International Trade Agreements
Negotiation of Trade Agreements: Sustainable development goals are increasingly becoming a component of international trade agreements. India must navigate trade agreements that include sustainability clauses and environmental standards. For instance, the EU-India Trade and Technology Council (TTC) discusses sustainability and digital trade, affecting how India negotiates and implements trade deals.
Compliance with Global Standards: India must ensure that its industries comply with international environmental standards to avoid trade barriers. For example, the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) imposes carbon tariffs on imports from countries with less stringent climate policies, impacting Indian exports in sectors like steel and cement.
Opportunities for Green Trade: India can leverage international trade agreements to promote its sustainable products and technologies. The India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is expected to include provisions for promoting trade in green goods and services, providing opportunities for Indian companies in the renewable energy sector.
Government Policies to Address Emerging Challenges
Promotion of Green Technologies: The government has launched several initiatives to support green technology and sustainable development. The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) focus on improving environmental quality and infrastructure, attracting foreign investment and enhancing export potential in green sectors.
Support for Export Diversification: The Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023-28 emphasizes the promotion of sustainable exports and diversification into high-value, eco-friendly products. The Development Commissioner (DC) of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) supports companies in adopting green practices and technologies to meet international standards.
Enhancing Compliance with International Standards: The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) work towards aligning domestic regulations with international standards. The National Action Plan on Climate Change outlines strategies for improving compliance with global environmental standards, which helps in reducing trade barriers and enhancing competitiveness.
Strengthening Trade Diplomacy: The government is actively engaged in trade diplomacy to incorporate sustainability clauses into trade agreements and negotiate terms that align with India’s development goals. Participation in global forums such as the UNFCCC and World Trade Organization (WTO) helps India address trade-related environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The growing emphasis on sustainable and climate-friendly development significantly impacts India’s external sector, influencing export diversification, foreign investment flows, and international trade agreements. While these changes present challenges, they also offer opportunities for growth in green sectors and sustainable technologies. The government’s policies to promote green technologies, support export diversification, ensure compliance with international standards, and strengthen trade diplomacy are crucial in addressing these emerging challenges and positioning India as a leader in sustainable development on the global stage.
See less
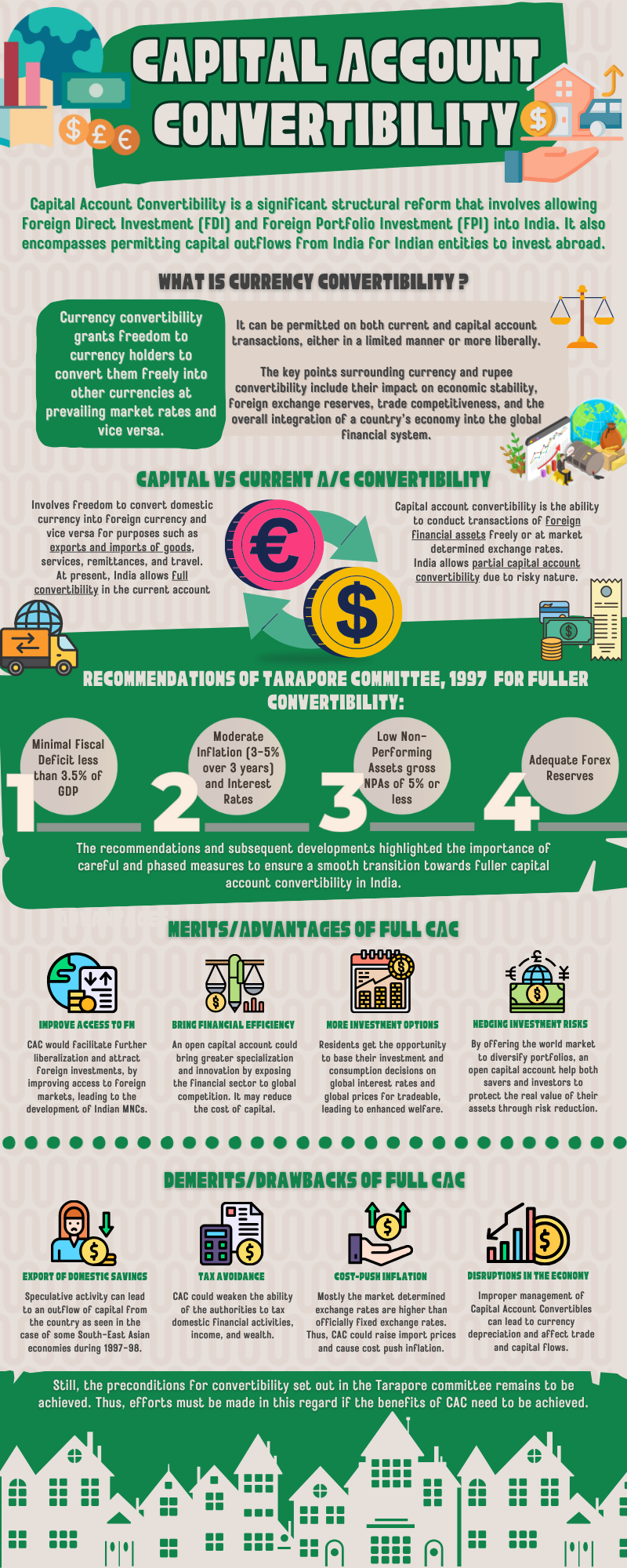
The Indian government has undertaken several initiatives to promote the internationalization of the Indian rupee (INR), with the aim of reducing external sector vulnerabilities and enhancing the country's global economic influence. Efforts to Expand the Use of INR in Trade and Investment TransactionRead more
The Indian government has undertaken several initiatives to promote the internationalization of the Indian rupee (INR), with the aim of reducing external sector vulnerabilities and enhancing the country’s global economic influence.
Efforts to Expand the Use of INR in Trade and Investment Transactions:
1.Trade Settlement in INR:
2. Liberalization of INR Convertibility:
3. Promoting INR-Denominated Bonds:
4. Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements:
Potential Impact on Reducing External Sector Vulnerabilities and Enhancing Global Influence:
1. Reducing Dependence on the US Dollar:
2. Improved Balance of Payments:
3. Strengthening India’s Global Economic Influence:
4. Geopolitical Advantages:
While the government’s efforts to promote the internationalization of the INR are commendable, the process is gradual and faces several challenges, such as the dominance of the US dollar, the limited convertibility of the INR, and the need for deeper financial market development. Sustained and comprehensive reforms, as well as strategic partnerships with other countries, will be crucial to enhance the global acceptance and usage of the Indian rupee and realize its full potential in reducing external sector vulnerabilities and strengthening India’s global economic influence.
See less