Soil pH regulates many chemical and biochemical reactions of soil that control nutrient absorption, plant growth, and productivity. Careful management of soil pH is necessary for soil vitality, crop yield, and quality. Each nutrient exhibits varying levels of solubility across the pH spectrum. HenceRead more
Soil pH regulates many chemical and biochemical reactions of soil that control nutrient absorption, plant growth, and productivity. Careful management of soil pH is necessary for soil vitality, crop yield, and quality. Each nutrient exhibits varying levels of solubility across the pH spectrum. Hence, it is necessary to maintain optimum soil pH for healthy plant growth.
a)Acidic Soil – (pH <7)
Soil acidity leads to reduced availability of various soil nutrients and toxicity of some . The nutrients applied through organic matter or fertilizers are either present in inaccessible form or eroded through leaching. The ability of microorganisms to degrade organic matter decreases dramatically.
b)Alkaline Soil – (pH >7)
Due to the high pH level, the soil often lacks nutrients like Fe, Zn, Mn, and Cu despite the high mineral content. It causes certain minerals to become chemically bound in the soil, making them less available to crops and resulting in poor growth and productivity
c)The physical, chemical, and biological aspects of soil improve with a pH nearly neutral.
d)Undesirable soil pH also leads to – (a) Poor flower and fruit setting (b) Nutrient deficiencies in crops (c) Abnormal leaf pigmentation (d) Insufficient nodulation in legumes (e) Decline in beneficial microbes population and rise in pathogenic organisms
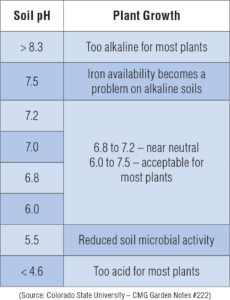
Effect of soil pH on plant growth

Agroecology refers to the application of ecological principles to agricultural systems,focusing on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. It encompasses a wide range of techniques that aim to enhance biodiversity, promote soil health, and reduce dependency on chemical inputs, Some imporRead more
Agroecology refers to the application of ecological principles to agricultural systems,focusing on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. It encompasses a wide range of techniques that aim to enhance biodiversity, promote soil health, and reduce dependency on chemical inputs, Some important steps are mentioned below:
Crop diversification can be further classified as
Improved structural diversity:- helps in making crops within the field more structurally diverse which potentially help in pest suppression and Genetics diversification in monoculture leads to cultivation of mixture of varieties of same species in a monoculture which help in disease suppression, and increases the production stability.
Agroforestry has been proved nothing but a boon to us as it is used for several agroecological ways in terms of growing crops and trees together either in spatial or temporal diversity benefitting pest suppression and climate change buffering.
Mixed landscapes has also been a great potential for development of large scale diversified landscapes through mixture of crops and cropping system with multiple ecosystems.
Micro-watershed based diversification has helped in integration of crops with other farming components for years round income and employment generation, besides sustaing soil and environmental health.
These principles not only gives emphasis to the quality production of crops but also ensures that the pest management and ideation of microclimate is done in a most sustainable way.
See less