Effective disaster management in urban areas, particularly in the context of increasing climate-related events like heatwaves and floods, involves a multifaceted approach that considers several key factors: Risk Assessment and Mapping: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify and map the vRead more
Effective disaster management in urban areas, particularly in the context of increasing climate-related events like heatwaves and floods, involves a multifaceted approach that considers several key factors:
- Risk Assessment and Mapping:
- Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify and map the vulnerabilities of urban areas to various climate-related disasters.
- This includes analyzing factors such as geography, infrastructure, population density, and socioeconomic conditions.
- Robust Early Warning Systems:
- Develop early warning systems that can detect and provide timely alerts about the onset of climate-related events, allowing for proactive preparedness and response.
- Leverage advanced technologies, such as real-time monitoring, satellite data, and weather forecasting, to enhance the accuracy and reliability of these systems.
- Resilient Infrastructure and Urban Planning:
- Incorporate climate change adaptation measures into urban planning and infrastructure development, such as:
- Designing flood-resistant buildings and transportation systems
- Investing in green infrastructure (e.g., urban forests, green spaces) to mitigate the urban heat island effect
- Ensuring adequate drainage systems and water management facilities
- Incorporate climate change adaptation measures into urban planning and infrastructure development, such as:
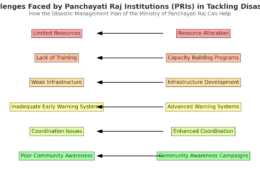
- Community Engagement and Capacity Building:
- Actively engage with local communities to raise awareness about climate-related risks and foster a culture of preparedness.
- Empower communities to develop disaster response plans and participate in emergency drills and simulation exercises.
- Provide training and capacity-building programs for community members, including vulnerable populations, to enhance their resilience.
- Effective Coordination and Collaboration:
- Establish clear communication channels and coordination mechanisms among various stakeholders, including government agencies, emergency responders, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector.
- Develop comprehensive disaster management plans that outline roles, responsibilities, and protocols for effective response and recovery efforts.
- Integrated Data Management and Technology Adoption:
- Utilize data-driven decision-making by collecting, analyzing, and sharing reliable data on climate-related risks and disaster impacts.
- Adopt innovative technologies, such as geospatial mapping, remote sensing, and predictive analytics, to enhance situational awareness and inform disaster management strategies.

First we need to understand the terms disaster here which simply means- "any hazardous or catastrophic event which has consequential impact on the lives of the people and living beings. Disaster could be natural or human induced disasters, for eg: Tsunami, earthquake, fires, chemical disaster etc NoRead more
First we need to understand the terms disaster here which simply means- “any hazardous or catastrophic event which has consequential impact on the lives of the people and living beings. Disaster could be natural or human induced disasters, for eg: Tsunami, earthquake, fires, chemical disaster etc
Now we need to understand the key components of disaster management plan.
So, it could be betterly understand from the cyclic concept of disaster management where it emphasis on the two broader aspects of it- Pre-disaster management and post-disaster management plans.
Pre-disaster management includes the two major key components- preparedness and mitigation measures.
1. Assessment– it includes the proper assessment of that region in terms of risk factors and vulnerability it possesses from the future disasters based on that data priority should be placed.
2. Planning or preparedness– it’s a wider scope to understand as it involves all the major activities which helps the local people to prepare themselves for the disaster. So it involves policy making, resources placement according to vulnerability of the region, infrastructure and capacity building.
Post-disaster management involves three significant features- response, recovery and rehabilitation.
It’s an event which starts just after the disaster hits the region so this phase is so crucial from the point of view of the casuality and damages to the ecosystem.
1. Response– it involves the catering the emergency needs of the people affected from the disaster which incorporates- providing medical supplies, temporary homes, clothes and shelter, logistics support, clean food and water supply etc.
2. Recovery or rehabilitation– it is also crucial phase as it involves the rebuilding of the lives of people affected from the disaster who lost everything in that disaster. Infrastructure rebuilding– roads, hospital, education centre etc, debris cleaning which has been accumulated from the disaster, economy rebuilding– providing them jobs and means of earning source considering long term impacts, and planning to learn from the disaster to prevent or reduce the vulnerability of the region in future.
This both phase constitutes significance in itself from the point of view of the disaster hitting a region from reducing its vulnerability to rebuilding the infrastructure incorporates lots of planning, execution and cooperation.
The basic difference between the natural and human induced disaster is that we can’t predict the disastrous events in the natural disaster but in the human one can predict the event due to the human errors made during the operation part. So the planning becomes quite easy while preparing for the human induced disaster as it would be more accurate in terms of its predictability.
In terms of its responsiveness, the difference are not that much because it totally depends on the how intense and large area it had impacted, so on that basis both can be wide spread and narrowly impact on the area.
See less